Flute Sheet Music
 "Why waste money on psychotherapy when you can listen to the B Minor Mass? " Michael Torke
"Why waste money on psychotherapy when you can listen to the B Minor Mass? " Michael Torke
Gruber, Franz Xaver

Franz Xaver Gruber (25 November 1787 – 7 June 1863), was an Austrian primary school teacher, church organist and composer in the village of Arnsdorf, who is best known for composing the music to "Stille Nacht" ("Silent Night").
Contents
1 Life
2 "Silent Night"
3 Family
4 References
5 External links
Life
Gruber was born on 25 November 1787 in the village of Hochburg-Ach, Upper Austria, the son of linen weavers, Josef and Maria Gruber. His given name was recorded in the baptismal record as "Conrad Xavier," but this was later changed to "Franz Xaver". The Hochburger schoolteacher Andreas Peterlechner gave him music lessons.
Gruber taught at the primary school in Arnsdorf
Portrait in the Silent Night Chapel in Oberndorf bei Salzburg
Silent Night
Choral version by United States Army Chorus
Problems playing this file? See media help.
Gruber worked as a weaver until the age of 18, then trained to become a schoolteacher. He completed his music education studying with the church organist of Burghausen, Georg Hartdobler. In 1807 Gruber became a schoolteacher in Arnsdorf. He also became the church caretaker and organist. In 1808 he married a widow, Maria Elisabeth Fischinger Engelsberger. They had two children, both of whom died young. After the death of his first wife in 1825, Gruber married a former student, Maria Breitfuss. They had ten children, four of whom survived to adulthood. In 1829 Gruber moved to Berndorf, and in later years to Hallein, Salzburg, where he was named choir director, singer and organist.
Maria Gruber died in childbirth in 1841. The following year he married Katherine Wimmer.
Contents
1 Life
2 "Silent Night"
3 Family
4 References
5 External links
Life
Gruber was born on 25 November 1787 in the village of Hochburg-Ach, Upper Austria, the son of linen weavers, Josef and Maria Gruber. His given name was recorded in the baptismal record as "Conrad Xavier," but this was later changed to "Franz Xaver". The Hochburger schoolteacher Andreas Peterlechner gave him music lessons.
Gruber taught at the primary school in Arnsdorf
Portrait in the Silent Night Chapel in Oberndorf bei Salzburg
Silent Night
Choral version by United States Army Chorus
Problems playing this file? See media help.
Gruber worked as a weaver until the age of 18, then trained to become a schoolteacher. He completed his music education studying with the church organist of Burghausen, Georg Hartdobler. In 1807 Gruber became a schoolteacher in Arnsdorf. He also became the church caretaker and organist. In 1808 he married a widow, Maria Elisabeth Fischinger Engelsberger. They had two children, both of whom died young. After the death of his first wife in 1825, Gruber married a former student, Maria Breitfuss. They had ten children, four of whom survived to adulthood. In 1829 Gruber moved to Berndorf, and in later years to Hallein, Salzburg, where he was named choir director, singer and organist.
Maria Gruber died in childbirth in 1841. The following year he married Katherine Wimmer.
Chopin

Frédéric Chopin (1 March 1810 – 17 October 1849) was a Polish composer and virtuoso pianist of the Romantic period. He is widely regarded as the greatest Polish composer, and ranks as one of music's greatest tone poets.
He was born in the village of Żelazowa Wola, in the Duchy of Warsaw, to a Polish mother and French-expatriate father, and in his early life was regarded as a child-prodigy pianist. In November 1830, at the age of 20, Chopin went abroad; following the suppression of the Polish November Uprising of 1830–31, he became one of many expatriates of the Polish "Great Emigration."
In Paris, he made a comfortable living as a composer and piano teacher, while giving few public performances. A Polish patriot,
Chopin's extant compositions were written primarily for the piano as a solo instrument. Though technically demanding, Chopin's style emphasizes nuance and expressive depth rather than virtuosity. Chopin invented musical forms such as the ballade and was responsible for major innovations in forms such as the piano sonata, waltz, nocturne, étude, impromptu and prelude. His works are mainstays of Romanticism in 19th-century classical music.
He was born in the village of Żelazowa Wola, in the Duchy of Warsaw, to a Polish mother and French-expatriate father, and in his early life was regarded as a child-prodigy pianist. In November 1830, at the age of 20, Chopin went abroad; following the suppression of the Polish November Uprising of 1830–31, he became one of many expatriates of the Polish "Great Emigration."
In Paris, he made a comfortable living as a composer and piano teacher, while giving few public performances. A Polish patriot,
Chopin's extant compositions were written primarily for the piano as a solo instrument. Though technically demanding, Chopin's style emphasizes nuance and expressive depth rather than virtuosity. Chopin invented musical forms such as the ballade and was responsible for major innovations in forms such as the piano sonata, waltz, nocturne, étude, impromptu and prelude. His works are mainstays of Romanticism in 19th-century classical music.
John Coltrane

John William "Trane" Coltrane (September 23, 1926 – July 17, 1967) was an American jazz saxophonist and composer.
Working in the bebop and hard bop idioms early in his career, Coltrane helped pioneer the use of modes in jazz and later was at the forefront of free jazz. He was prolific, making about fifty recordings as a leader during his recording career, and appeared as a sideman on many other albums, notably with trumpeter Miles Davis and pianist Thelonious Monk. As his career progressed, Coltrane's music took on an increasingly spiritual dimension. His second wife was pianist Alice Coltrane, and their son Ravi Coltrane is also a saxophonist.
He influenced innumerable musicians, and remains one of the most significant tenor saxophonists in jazz history. He received many awards, among them a posthumous Special Citation from the Pulitzer Prize Board in 2007 for his "masterful improvisation, supreme musicianship and iconic centrality to the history of jazz."
Working in the bebop and hard bop idioms early in his career, Coltrane helped pioneer the use of modes in jazz and later was at the forefront of free jazz. He was prolific, making about fifty recordings as a leader during his recording career, and appeared as a sideman on many other albums, notably with trumpeter Miles Davis and pianist Thelonious Monk. As his career progressed, Coltrane's music took on an increasingly spiritual dimension. His second wife was pianist Alice Coltrane, and their son Ravi Coltrane is also a saxophonist.
He influenced innumerable musicians, and remains one of the most significant tenor saxophonists in jazz history. He received many awards, among them a posthumous Special Citation from the Pulitzer Prize Board in 2007 for his "masterful improvisation, supreme musicianship and iconic centrality to the history of jazz."
James Brown

James Joseph Brown, Jr. (May 3, 1933 – December 25, 2006), commonly referred to as "The Godfather of Soul", "King of Funk", and "The Hardest Working Man in Show Business", was an American entertainer. He is recognized as one of the most influential figures in 20th century popular music and was renowned for his vocals, and feverish dancing.
As a prolific singer, songwriter, bandleader, Brown was a pivotal force in the music industry. He left his mark on numerous artists. Brown's music also left its mark on the rhythms of African popular music, such as afrobeat, jùjú and mbalax, and provided a template for go-go music.
Brown began his professional music career in 1953, and rose to fame during the late 1950s and early 1960s on the strength of his thrilling live performances and string of smash hits. In spite of various personal problems and setbacks he continued to score hits in every decade through the 1980s. In addition to his acclaim in music, Brown was a presence in American political affairs during the 1960s and 1970s, noted especially for his activism on behalf of fellow African Americans and the poor. During the early 1980s, Brown's music helped to shape the rhythms of early hip-hop music, with numerous groups looping or sampling his funk grooves and turning them into what became hip hop classics and the foundations of the music genre.
Brown was recognized by numerous titles, including Soul Brother Number One, Sex Machine, Mr. Dynamite, The Hardest Working Man in Show Business, Minister of The New New Super Heavy Funk, Mr. Please Please Please, The Boss, and the best-known, the Godfather of Soul.
As a prolific singer, songwriter, bandleader, Brown was a pivotal force in the music industry. He left his mark on numerous artists. Brown's music also left its mark on the rhythms of African popular music, such as afrobeat, jùjú and mbalax, and provided a template for go-go music.
Brown began his professional music career in 1953, and rose to fame during the late 1950s and early 1960s on the strength of his thrilling live performances and string of smash hits. In spite of various personal problems and setbacks he continued to score hits in every decade through the 1980s. In addition to his acclaim in music, Brown was a presence in American political affairs during the 1960s and 1970s, noted especially for his activism on behalf of fellow African Americans and the poor. During the early 1980s, Brown's music helped to shape the rhythms of early hip-hop music, with numerous groups looping or sampling his funk grooves and turning them into what became hip hop classics and the foundations of the music genre.
Brown was recognized by numerous titles, including Soul Brother Number One, Sex Machine, Mr. Dynamite, The Hardest Working Man in Show Business, Minister of The New New Super Heavy Funk, Mr. Please Please Please, The Boss, and the best-known, the Godfather of Soul.
GEORG PHILLIP TELEMANN

Georg Philipp Telemann (24 March 1681 – 25 June 1767) (German pronunciation: ) was a German Baroque composer and multi-instrumentalist. Almost completely self-taught in music, he became a composer against his family's wishes. After studying in Magdeburg, Zellerfeld, and Hildesheim, Telemann entered the University of Leipzig to study law, but eventually settled on a career in music. He held important positions in Leipzig, Sorau, Eisenach, and Frankfurt before settling in Hamburg in 1721, where he became musical director of that city's five main churches. While Telemann's career prospered, his personal life was always troubled: his first wife died less than two years after their marriage, and his second wife had extramarital affairs and accumulated a large gambling debt before leaving him.
Bach

Johann Sebastian Bach (31 March 1685 – 28 July 1750) was a German composer and organist whose sacred and secular works for choir, orchestra, and solo instruments drew together the strands of the Baroque period and brought it to its ultimate maturity. Although he introduced no new forms, he enriched the prevailing German style with a robust contrapuntal technique, an unrivalled control of harmonic and motivic organisation in composition for diverse musical forces, and the adaptation of rhythms and textures from abroad, particularly Italy and France.
Revered for their intellectual depth and technical and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg concertos; the Goldberg Variations; the English Suites, French Suites, Partitas, and Well-Tempered Clavier; the Mass in B Minor; the St. Matthew Passion; the St. John Passion; The Musical Offering; The Art of Fugue; the Sonatas and Partitas for violin solo; the Cello Suites; more than 200 surviving cantatas; and a similar number of organ works, including the celebrated Toccata and Fugue in D Minor.
While Bach's fame as an organist was great during his lifetime, he was not particularly well-known as a composer. His adherence to Baroque forms and contrapuntal style was considered "old-fashioned" by his contemporaries, especially late in his career when the musical fashion tended towards Rococo and later Classical styles. A revival of interest and performances of his music began early in the 19th century, and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
Revered for their intellectual depth and technical and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg concertos; the Goldberg Variations; the English Suites, French Suites, Partitas, and Well-Tempered Clavier; the Mass in B Minor; the St. Matthew Passion; the St. John Passion; The Musical Offering; The Art of Fugue; the Sonatas and Partitas for violin solo; the Cello Suites; more than 200 surviving cantatas; and a similar number of organ works, including the celebrated Toccata and Fugue in D Minor.
While Bach's fame as an organist was great during his lifetime, he was not particularly well-known as a composer. His adherence to Baroque forms and contrapuntal style was considered "old-fashioned" by his contemporaries, especially late in his career when the musical fashion tended towards Rococo and later Classical styles. A revival of interest and performances of his music began early in the 19th century, and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
Tamiya Terashima

Tamiya Terashima Composer Born: April 10, 1958 (age 64 years), Kumamoto, Japan Albums: Gedo Senki (Tales From Earthsee),
Joachim Andersen

Carl Joachim Andersen (April 29, 1847 – May 7, 1909) was a Danish flutist, conductor and composer born in Copenhagen, son of the flutist Christian Joachim Andersen. Both as a virtuoso and as composer of flute music, he is considered one of the best of his time. He was a tough leader and teacher and demanded as such a lot from his orchestras but through that style he reached a high level.
Dukas

Paul Abraham Dukas (1 October 1865 – 17 May 1935) was a French composer, critic, scholar and teacher. A studious man, of retiring personality, he was intensely self-critical, and he abandoned and destroyed many of his compositions. His best known work is the orchestral piece The Sorcerer's Apprentice (L'apprenti sorcier), the fame of which has eclipsed that of his other surviving works. Among these are an opera Ariane et Barbe-bleue, a symphony, two substantial works for solo piano, and a ballet, La Péri.
At a time when French musicians were divided into conservative and progressive factions, Dukas adhered to neither but retained the admiration of both. His compositions were influenced by composers including Beethoven, Berlioz, Franck, d'Indy and Debussy.
In tandem with his composing career, Dukas worked as a music critic, contributing regular reviews to at least five French journals. Later in his life he was appointed professor of composition at the Conservatoire de Paris and the École Normale de Musique; his pupils included Maurice Duruflé, Olivier Messiaen, Manuel Ponce, and Joaquín Rodrigo.
At a time when French musicians were divided into conservative and progressive factions, Dukas adhered to neither but retained the admiration of both. His compositions were influenced by composers including Beethoven, Berlioz, Franck, d'Indy and Debussy.
In tandem with his composing career, Dukas worked as a music critic, contributing regular reviews to at least five French journals. Later in his life he was appointed professor of composition at the Conservatoire de Paris and the École Normale de Musique; his pupils included Maurice Duruflé, Olivier Messiaen, Manuel Ponce, and Joaquín Rodrigo.
Era

Era is a new-age music project by French composer Eric Lévi. Some of the lyrics were written by Guy Protheroe in an imaginary language similar to Greek or Latin, but deliberately devoid of any exact meaning.
Carl Neilson

Carl August Nielsen was a Danish composer, conductor and violinist, widely recognized as his country's most prominent composer. Brought up by poor yet musically talented parents on the island of Funen, he demonstrated his musical abilities at an early age.
Traditional

John Williams

John Towner Williams (born February 8, 1932) is an American composer, conductor, and pianist. In a career that spans six decades, Williams has composed many of the most famous film scores in Hollywood history, including Star Wars, Superman, Home Alone, the first three Harry Potter movies and all but two of Steven Spielberg's feature films including the Indiana Jones series, Schindler's List, E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial, Jurassic Park and Jaws. He also composed the soundtrack for the hit 1960s television series Lost in Space as well as the fanfare of the DreamWorks Pictures' logo.
Williams has composed theme music for four Olympic Games, the NBC Nightly News, the rededication of the Statue of Liberty, and numerous television series and concert pieces. He served as the principal conductor of the Boston Pops Orchestra from 1980 to 1993, and is now the orchestra's laureate conductor.
Williams is a five-time winner of the Academy Award. He has also won four Golden Globe Awards, seven BAFTA Awards and 21 Grammy Awards. With 45 Academy Award nominations, Williams is, together with composer Alfred Newman, the second most nominated person after Walt Disney. He was inducted into the Hollywood Bowl Hall of Fame in 2000, and was a recipient of the Kennedy Center Honors in 2004.
Williams has composed theme music for four Olympic Games, the NBC Nightly News, the rededication of the Statue of Liberty, and numerous television series and concert pieces. He served as the principal conductor of the Boston Pops Orchestra from 1980 to 1993, and is now the orchestra's laureate conductor.
Williams is a five-time winner of the Academy Award. He has also won four Golden Globe Awards, seven BAFTA Awards and 21 Grammy Awards. With 45 Academy Award nominations, Williams is, together with composer Alfred Newman, the second most nominated person after Walt Disney. He was inducted into the Hollywood Bowl Hall of Fame in 2000, and was a recipient of the Kennedy Center Honors in 2004.
Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach

Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach (8 March 1714 – 14 December 1788) was a German musician and composer, the second of three sons of Johann Sebastian Bach and Maria Barbara Bach. He was a crucial composer in the transition between the Baroque and Classical periods, and one of the founders of the Classical style, composing in the Rococo and Classical periods. His second name was given in honor of Georg Philipp Telemann, a friend of Emanuel's father and his godfather.
Through the latter half of the 18th century, the reputation of Emanuel Bach stood very high. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart said of him, "He is the father, we are the children." The best part of Joseph Haydn's training was derived from a study of his work. Ludwig van Beethoven expressed for his genius the most cordial admiration and regard. This position he owes mainly to his keyboard sonatas, which mark an important epoch in the history of musical form. Lucid in style, delicate and tender in expression, they are even more notable for the freedom and variety of their structural design; they break away altogether from both the Italian and the Viennese schools, moving instead toward the cyclical and improvisatory forms that would become common several generations later.
The content of his work is full of invention and, most importantly, extreme unpredictability, and wide emotional range even within a single work, a style that may be categorised as Empfindsamer Stil. It is no less sincere in thought than polished and felicitous in phrase. He was probably the first composer of eminence who made free use of harmonic colour for its own sake since the time of Lassus, Monteverdi, and Gesualdo. In this way, he compares well with the most important representatives of the First Viennese School. In fact he exerted enormous influence on the North German School of composers, in particular Georg Anton Benda, Bernhard Joachim Hagen, Ernst Wilhelm Wolf, Johann Gottfried Müthel, Friedrich Wilhelm Rust and many others. His influence was not limited to his contemporaries, and extended to Felix Mendelssohn and Carl Maria von Weber.
Through the latter half of the 18th century, the reputation of Emanuel Bach stood very high. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart said of him, "He is the father, we are the children." The best part of Joseph Haydn's training was derived from a study of his work. Ludwig van Beethoven expressed for his genius the most cordial admiration and regard. This position he owes mainly to his keyboard sonatas, which mark an important epoch in the history of musical form. Lucid in style, delicate and tender in expression, they are even more notable for the freedom and variety of their structural design; they break away altogether from both the Italian and the Viennese schools, moving instead toward the cyclical and improvisatory forms that would become common several generations later.
The content of his work is full of invention and, most importantly, extreme unpredictability, and wide emotional range even within a single work, a style that may be categorised as Empfindsamer Stil. It is no less sincere in thought than polished and felicitous in phrase. He was probably the first composer of eminence who made free use of harmonic colour for its own sake since the time of Lassus, Monteverdi, and Gesualdo. In this way, he compares well with the most important representatives of the First Viennese School. In fact he exerted enormous influence on the North German School of composers, in particular Georg Anton Benda, Bernhard Joachim Hagen, Ernst Wilhelm Wolf, Johann Gottfried Müthel, Friedrich Wilhelm Rust and many others. His influence was not limited to his contemporaries, and extended to Felix Mendelssohn and Carl Maria von Weber.
TV Theme Band

TV Theme Band Musical artist Genre: Soundtracks Albums: The Greatest TV Themes - Sitcom Series, Record labels: Juicy Life Records, BOSS MUSIC, MORE Songs Jeopardy Theme Song Classic Tv Themes - The Best of Tv Game Shows · 2010
The Flintstones Theme Song Classic Tv Themes - The Best of Kids Cartoons · 2010 Bear in the Big Blue House Theme Song Classic Tv Themes - The Best of Kid.
The Flintstones Theme Song Classic Tv Themes - The Best of Kids Cartoons · 2010 Bear in the Big Blue House Theme Song Classic Tv Themes - The Best of Kid.
Sailor Moon

Sailor Moon is the title of a Japanese media franchise created by Naoko Takeuchi. It is generally credited with popularizing the concept of a sentai (team) of magical girls, as well as the general re-emergence of the magical girl genre itself.
The story of the various metaseries revolves around the reincarnated defenders of a kingdom that once spanned the solar system, and the evil forces that they battle. The major characters—called Sailor Senshi (literally "Sailor Soldiers"; frequently called "Sailor Scouts" in the North American version)—are teenage girls who can transform into heroines named for the moon and planets (Sailor Moon, Sailor Mercury, Sailor Mars, etc). The use of "Sailor" comes from a style of girls' school uniform popular in Japan, the sērā fuku (sailor outfit), after which the Senshi's uniforms are modeled. The elements of fantasy in the series are heavily symbolic and often based on mythology.
Music for the Sailor Moon metaseries was written and composed by numerous people, including frequent lyrical contributions by creator Naoko Takeuchi. All of the background musical scores, including the spinoffs, games, and movies, were composed and arranged by Takanori Arisawa, who earned the "Golden Disk Grand Prize" from Columbia Records for his work on the first series soundtrack in 1993. In 1998, 2000, and 2001 he won the JASRAC International Award for most international royalties, owing largely to the popularity of Sailor Moon music in other nations.
The story of the various metaseries revolves around the reincarnated defenders of a kingdom that once spanned the solar system, and the evil forces that they battle. The major characters—called Sailor Senshi (literally "Sailor Soldiers"; frequently called "Sailor Scouts" in the North American version)—are teenage girls who can transform into heroines named for the moon and planets (Sailor Moon, Sailor Mercury, Sailor Mars, etc). The use of "Sailor" comes from a style of girls' school uniform popular in Japan, the sērā fuku (sailor outfit), after which the Senshi's uniforms are modeled. The elements of fantasy in the series are heavily symbolic and often based on mythology.
Music for the Sailor Moon metaseries was written and composed by numerous people, including frequent lyrical contributions by creator Naoko Takeuchi. All of the background musical scores, including the spinoffs, games, and movies, were composed and arranged by Takanori Arisawa, who earned the "Golden Disk Grand Prize" from Columbia Records for his work on the first series soundtrack in 1993. In 1998, 2000, and 2001 he won the JASRAC International Award for most international royalties, owing largely to the popularity of Sailor Moon music in other nations.
John Mackey

John Mackey (born October 1, 1973) is an American composer of contemporary classical music, with an emphasis on music for wind band, as well as orchestra. For several years, he focused on music for modern dance and ballet.John Mackey was born in New Philadelphia, Ohio and grew up in Westerville, Ohio, where he attended Westerville South High School. Though musicians themselves, Mackey's parents did not provide him with music lessons, and he never formally studied an instrument. His grandfather, however, taught him to read music and introduced him to digital music notation.
Claude Bolling

Claude Bolling (born 10 April 1930), is a renowned French jazz pianist, composer, arranger, and occasional actor.
He was born in Cannes, studied at the Nice Conservatory, then in Paris. A child prodigy, by age 14 he was playing jazz piano professionally, with Lionel Hampton, Roy Eldridge, and Kenny Clarke. Bolling's books on jazz technique show that he did not delve far beyond bebop into much avant garde jazz. He was a major part of the traditional jazz revival in the late 1960s, and he became friends with Oscar Peterson.
He has written music for over one hundred films, mostly French, starting with the score for a 1957 documentary about the Cannes Film Festival, and including the films Borsalino (1970), and California Suite (1978).
Bolling is also noted for a series of "crossover" collaborations with classical musicians. His Suite for Flute and Jazz Piano Trio with Jean-Pierre Rampal, a mix of Baroque elegance with modern swing, has been a top seller for many years, and was followed up by other works in the same vein. It was particularly popular in the United States, at the top of the hit parade for two years after its release and on billboard top 40 for 530 weeks, roughly ten years.
Following his work with Rampal, Bolling went on to work with many other musicians, from different genres, including Alexandre Lagoya, Pinchas Zukerman, Maurice André, and Yo-Yo Ma. He has also worked with, and performed tributes to many others, including Lionel Hampton, Duke Ellington, Stéphane Grappelli, Django Reinhardt, Oscar Peterson.
He was born in Cannes, studied at the Nice Conservatory, then in Paris. A child prodigy, by age 14 he was playing jazz piano professionally, with Lionel Hampton, Roy Eldridge, and Kenny Clarke. Bolling's books on jazz technique show that he did not delve far beyond bebop into much avant garde jazz. He was a major part of the traditional jazz revival in the late 1960s, and he became friends with Oscar Peterson.
He has written music for over one hundred films, mostly French, starting with the score for a 1957 documentary about the Cannes Film Festival, and including the films Borsalino (1970), and California Suite (1978).
Bolling is also noted for a series of "crossover" collaborations with classical musicians. His Suite for Flute and Jazz Piano Trio with Jean-Pierre Rampal, a mix of Baroque elegance with modern swing, has been a top seller for many years, and was followed up by other works in the same vein. It was particularly popular in the United States, at the top of the hit parade for two years after its release and on billboard top 40 for 530 weeks, roughly ten years.
Following his work with Rampal, Bolling went on to work with many other musicians, from different genres, including Alexandre Lagoya, Pinchas Zukerman, Maurice André, and Yo-Yo Ma. He has also worked with, and performed tributes to many others, including Lionel Hampton, Duke Ellington, Stéphane Grappelli, Django Reinhardt, Oscar Peterson.
Moe Koffman

Morris "Moe" Koffman, OC was a Canadian jazz saxophonist and flautist, as well as composer and arranger. During a career spanning from the 1950s to the 2000s, Koffman was one of Canada's most prolific musicians, working variously in clubs and sessions and releasing 30 albums.
Beethoven

Ludwig van Beethoven (16 December 1770 - 26 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He was a crucial figure in the transitional period between the Classical and Romantic eras in Western classical music, and remains one of the most respected and influential composers of all time.
Born in Bonn, then in the Electorate of Cologne (now in modern-day Germany), he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. Beethoven's hearing gradually deteriorated beginning in his twenties, yet he continued to compose masterpieces, and to conduct and perform, even after he was completely deaf.
Born in Bonn, then in the Electorate of Cologne (now in modern-day Germany), he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. Beethoven's hearing gradually deteriorated beginning in his twenties, yet he continued to compose masterpieces, and to conduct and perform, even after he was completely deaf.
Danny Elfman

Daniel Robert "Danny" Elfman (born May 29, 1953) is an American musician, best known for composing music for television and movies, and leading the rock band Oingo Boingo as singer/songwriter from 1976 until its breakup in 1995. He is a frequent collaborator with long-time friend Tim Burton, and has scored all but two of his films. He was nominated for four Academy Awards and won a Grammy Award for Tim Burton's Batman and an Emmy Award for his Desperate Housewives theme. Elfman also wrote the theme for the video game Fable. He is also famous for creating The Simpsons main title theme, and his role as Jack Skellington's singing voice in The Nightmare Before Christmas. He is the Uncle in-law to actress Jenna Elfman.
Music theory

Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. The Oxford Companion to Music describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory"
Robert Valentine

Robert Valentine (c. 1671 – 26 May 1747), also known as Roberto Valentini and Roberto Valentino, was an English composer, recorder player, oboist and violinist, who moved to Rome and became a naturalised Italian. He is noted for his large number of compositions for the recorder.Born c. 1671, he was baptized in Leicester on 16 January 1674. He was the son of Thomas Follentine or Follintine, who lived in Leicester from c. 1670 and worked as a town musician there accompanied by his elder sons Thomas and Henry. The family became a prominent one in the musical life of Leicester; descendants included John Valentine, who was the grandson of Robert's eldest brother Thomas, and John Valentine's daughter Ann Valentine.
Ennio Morricone
Ennio Morricone, OMRI (born November 10, 1928), is an Italian composer and conductor. He has composed and arranged scores for more than 500 film and television productions. Morricone is considered as one of the most influential film composers since the late 1950s. He is well-known for his long-term collaborations with international acclaimed directors such as Sergio Leone, Brian De Palma, Barry Levinson, and Giuseppe Tornatore.
He wrote the characteristic film scores of Leone's Spaghetti Westerns A Fistful of Dollars (1964), For a Few Dollars More (1965), The Good, the Bad and the Ugly (1966), Once Upon a Time in the West (1968), The Great Silence (1968), and My Name Is Nobody (1973). In the 80s, Morricone composed the scores for John Carpenter's horror movie The Thing (1982), Leone's Once Upon a Time in America (1984), Roland Joffé's The Mission (1986), Brian De Palma's The Untouchables (1987) and Giuseppe Tornatore's Cinema Paradiso (1988).
His more recent compositions include the scores for Oliver Stone's U Turn (1997), Tornatore's The Legend of 1900 (1998) and Malèna (2000), Mission to Mars (2000) by Brian De Palma, Fateless (2005), and Baaria - La porta del vento (2009). Ennio Morricone has won two Grammy Awards, two Golden Globes and five Anthony Asquith Awards for Film Music by BAFTA in 1979–1992. He has been nominated for five Academy Awards for Best Music, Original Score in 1979–2001. Morricone received the Honorary Academy Award in 2007 "for his magnificent and multifaceted contributions to the art of film music". He was the second composer to receive this award after its introduction in 1928.
He wrote the characteristic film scores of Leone's Spaghetti Westerns A Fistful of Dollars (1964), For a Few Dollars More (1965), The Good, the Bad and the Ugly (1966), Once Upon a Time in the West (1968), The Great Silence (1968), and My Name Is Nobody (1973). In the 80s, Morricone composed the scores for John Carpenter's horror movie The Thing (1982), Leone's Once Upon a Time in America (1984), Roland Joffé's The Mission (1986), Brian De Palma's The Untouchables (1987) and Giuseppe Tornatore's Cinema Paradiso (1988).
His more recent compositions include the scores for Oliver Stone's U Turn (1997), Tornatore's The Legend of 1900 (1998) and Malèna (2000), Mission to Mars (2000) by Brian De Palma, Fateless (2005), and Baaria - La porta del vento (2009). Ennio Morricone has won two Grammy Awards, two Golden Globes and five Anthony Asquith Awards for Film Music by BAFTA in 1979–1992. He has been nominated for five Academy Awards for Best Music, Original Score in 1979–2001. Morricone received the Honorary Academy Award in 2007 "for his magnificent and multifaceted contributions to the art of film music". He was the second composer to receive this award after its introduction in 1928.
Jean-Baptiste Lully
Jean-Baptiste Lully (UK: /ˈlʊli/, US: /luːˈliː/; French: ; born Giovanni Battista Lulli, Italian: ; 28 November 1632 – 22 March 1687) was an Italian-born French composer, instrumentalist, and dancer who is considered a master of the French Baroque music style. Best known for his operas, he spent most of his life working in the court of Louis XIV of France and became a French subject in 1661.
Mozart

Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, full name Johann Chrysostom Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 â 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical era. His over 600 compositions include works widely acknowledged as pinnacles of symphonic, concertante, chamber, piano, operatic, and choral music. Mozart is among the most enduringly popular of classical composers, and many of his works are part of the standard concert repertoire.
Mozart's music, like Haydn's, stands as an archetypal example of the Classical style. His works spanned the period during which that style transformed from one exemplified by the style galant to one that began to incorporate some of the contrapuntal complexities of the late Baroque, complexities against which the galant style had been a reaction. Mozart's own stylistic development closely paralleled the development of the classical style as a whole. In addition, he was a versatile composer and wrote in almost every major genre, including symphony, opera, the solo concerto, chamber music including string quartet and string quintet, and the piano sonata. While none of these genres were new, the piano concerto was almost single-handedly developed and popularized by Mozart. He also wrote a great deal of religious music, including masses; and he composed many dances, divertimenti, serenades, and other forms of light entertainment.
The central traits of the classical style can be identified in Mozart's music. Clarity, balance, and transparency are hallmarks of his work.
Mozart's music, like Haydn's, stands as an archetypal example of the Classical style. His works spanned the period during which that style transformed from one exemplified by the style galant to one that began to incorporate some of the contrapuntal complexities of the late Baroque, complexities against which the galant style had been a reaction. Mozart's own stylistic development closely paralleled the development of the classical style as a whole. In addition, he was a versatile composer and wrote in almost every major genre, including symphony, opera, the solo concerto, chamber music including string quartet and string quintet, and the piano sonata. While none of these genres were new, the piano concerto was almost single-handedly developed and popularized by Mozart. He also wrote a great deal of religious music, including masses; and he composed many dances, divertimenti, serenades, and other forms of light entertainment.
The central traits of the classical style can be identified in Mozart's music. Clarity, balance, and transparency are hallmarks of his work.
CArl Friedrich Abel

Carl Friedrich Abel (22 December 1723 – 20 June 1787) was a German composer of the Classical era. He was a renowned player of the viola da gamba, and produced significant compositions for that instrument.Abel was born in Köthen, a small German city, where his father, Christian Ferdinand Abel, had worked for years as the principal viola da gamba and cello player in the court orchestra. In 1723 Abel senior became director of the orchestra, when the previous director, Johann Sebastian Bach, moved to Leipzig. The young Abel later boarded at St. Thomas School, Leipzig, where he was taught by Bach.
Ravel

Joseph-Maurice Ravel (March 7, 1875 – December 28, 1937) was a French composer of Impressionist music known especially for his melodies, orchestral and instrumental textures and effects. Much of his piano music, chamber music, vocal music and orchestral music has entered the standard concert repertoire.
Ravel's piano compositions, such as Jeux d'eau, Miroirs and Gaspard de la Nuit, demand considerable virtuosity from the performer, and his orchestral music, including Daphnis et Chloé and his arrangement of Modest Mussorgsky's Pictures at an Exhibition, uses a variety of sound and instrumentation very effectively.
Ravel is perhaps known best for his orchestral work, Boléro (1928), which he considered trivial and once described as "a piece for orchestra without music."
According to SACEM, Ravel's estate earns more royalties than that of any other French musician. According to international copyright law, Ravel's works are public domain since January 1, 2008 in most countries. In France, due to anomalous copyright law extensions to account for the two world wars, they will not enter the public domain until 2015.
Ravel's piano compositions, such as Jeux d'eau, Miroirs and Gaspard de la Nuit, demand considerable virtuosity from the performer, and his orchestral music, including Daphnis et Chloé and his arrangement of Modest Mussorgsky's Pictures at an Exhibition, uses a variety of sound and instrumentation very effectively.
Ravel is perhaps known best for his orchestral work, Boléro (1928), which he considered trivial and once described as "a piece for orchestra without music."
According to SACEM, Ravel's estate earns more royalties than that of any other French musician. According to international copyright law, Ravel's works are public domain since January 1, 2008 in most countries. In France, due to anomalous copyright law extensions to account for the two world wars, they will not enter the public domain until 2015.
Franz Doppler

Albert Franz Doppler, was a flute virtuoso and a composer best known for his flute music. He also wrote one German and several Hungarian operas for Budapest, all produced with great success. His ballet music was popular during his lifetime
Jasmine Choi

Jasmine Choi (born in Seoul, South Korea) is a Korean-born flutist, educated in the US, living in Austria.Raised in Daejeon, Choi studied at the Curtis Institute of Music and the Juilliard School, where her teachers included Julius Baker and Jeffrey Khaner, from 2000 to 2004. As a student in 2002, she was the senior division winner of the Albert M. Greenfield Student Competition, sponsored by the Philadelphia Orchestra. In 2006, Symphony Magazine included her as one of two flautists in their list of emerging artists.[4
Gustav Mahler

Gustav Mahler was an Austrian late-Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th century Austro-German tradition and the modernism of the early 20th century.
Taizé (Band)

Taizé - Music of Unity and Peace is the 2015 studio album by the ecumenical Taizé Community from the eponymous village in France. It was recorded in May and July 2014, and was released in March 2015, by the Deutsche Grammophon.
Kathryn Master

Kathryn Master composer,musician.
Nobuo Uematsu

Nobuo Uematsu (植松伸夫 Uematsu Nobuo?, born March 21, 1959) is a Japanese video game composer and musician, best known for scoring the majority of titles in the Final Fantasy series. He is regarded as one of the most famous and respected composers in the video game community. Uematsu is a self-taught musician; he began to play the piano at the age of eleven or twelve, with Elton John as his biggest influence.
Uematsu joined Square (later Square Enix) in 1985, where he met Final Fantasy creator Hironobu Sakaguchi. They have worked together on numerous titles, most notably the games in the Final Fantasy series. After nearly 20 years in the company, he left Square Enix in 2004 and founded his own company called Smile Please, as well as the music production company Dog Ear Records. He has since composed music as a freelancer for video games primarily developed by Square Enix and Sakaguchi's development studio Mistwalker.
A handful of soundtracks and arranged albums of Uematsu's game scores have been released. Pieces from his video game works have been performed in concerts worldwide, and numerous Final Fantasy concerts have also been held. He has worked with Grammy Award-winning conductor Arnie Roth on several of these concerts. In 2002, he formed a rock band with colleagues Kenichiro Fukui and Tsuyoshi Sekito called The Black Mages, in which Uematsu plays the keyboard. The band plays arranged rock versions of Uematsu's Final Fantasy compositions.
Uematsu joined Square (later Square Enix) in 1985, where he met Final Fantasy creator Hironobu Sakaguchi. They have worked together on numerous titles, most notably the games in the Final Fantasy series. After nearly 20 years in the company, he left Square Enix in 2004 and founded his own company called Smile Please, as well as the music production company Dog Ear Records. He has since composed music as a freelancer for video games primarily developed by Square Enix and Sakaguchi's development studio Mistwalker.
A handful of soundtracks and arranged albums of Uematsu's game scores have been released. Pieces from his video game works have been performed in concerts worldwide, and numerous Final Fantasy concerts have also been held. He has worked with Grammy Award-winning conductor Arnie Roth on several of these concerts. In 2002, he formed a rock band with colleagues Kenichiro Fukui and Tsuyoshi Sekito called The Black Mages, in which Uematsu plays the keyboard. The band plays arranged rock versions of Uematsu's Final Fantasy compositions.
Final Fantasy VII

Final Fantasy VII is a role-playing video game developed by Square for the PlayStation console. Released in 1997, it is the seventh main installment in the Final Fantasy series. Published in Japan by Square, it was released in the West by Sony Computer Entertainment, becoming the first in the series to be released in Europe. The game's story follows Cloud Strife, a mercenary who joins an eco-terrorist organization to stop the world-controlling megacorporation, Shinra, from using the planet's life essence as an energy source. Events send Cloud and his allies in pursuit of Sephiroth, a superhuman intent on destroying their planet. During the journey, Cloud builds close friendships with his party members, including Aerith Gainsborough, who holds the secret to saving their world.
Development on Final Fantasy VII began in 1994 for the Super NES. After delays and technical difficulties from experimenting on several platforms, Square ultimately moved development to the PlayStation, largely due to the advantages of the CD-ROM format. Veteran series staff returned, including series creator and producer Hironobu Sakaguchi, director Yoshinori Kitase, and composer Nobuo Uematsu. The title became the first in the series to use full motion video and 3D computer graphics, with most scenes using character models superimposed over pre-rendered backgrounds. Although the gameplay systems remained mostly unchanged from previous entries, Final Fantasy VII featured science fiction elements with a more realistic presentation. The scale of development was unprecedented at the time, with a combined development and marketing budget of over USD$80 million, and a staff of over 100.
Development on Final Fantasy VII began in 1994 for the Super NES. After delays and technical difficulties from experimenting on several platforms, Square ultimately moved development to the PlayStation, largely due to the advantages of the CD-ROM format. Veteran series staff returned, including series creator and producer Hironobu Sakaguchi, director Yoshinori Kitase, and composer Nobuo Uematsu. The title became the first in the series to use full motion video and 3D computer graphics, with most scenes using character models superimposed over pre-rendered backgrounds. Although the gameplay systems remained mostly unchanged from previous entries, Final Fantasy VII featured science fiction elements with a more realistic presentation. The scale of development was unprecedented at the time, with a combined development and marketing budget of over USD$80 million, and a staff of over 100.
Prokofiev

Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev (Russian: Сергей Сергеевич Прокофьев; Ukrainian: Сергій Сергійович Прокоф'єв) (27 April 1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, pianist and conductor who mastered numerous musical genres and came to be admired as one of the greatest composers of the 20th century.
Prokofiev was a soloist with the London Symphony Orchestra, conducted by Piero Coppola, in the first recording of his Piano Concerto No. 3, recorded in London by His Master's Voice in June 1932. Prokofiev also recorded some of his solo piano music for HMV in Paris in February 1935; these recordings were issued on CD by Pearl and Naxos. In 1938, he conducted the Moscow Philharmonic Orchestra in a recording of the second suite from his Romeo and Juliet ballet; this performance was also later released on LP and CD. Another reported recording with Prokofiev and the Moscow Philharmonic was of the First Violin Concerto with David Oistrakh as soloist; Everest Records later released this recording on an LP.
Prokofiev was a soloist with the London Symphony Orchestra, conducted by Piero Coppola, in the first recording of his Piano Concerto No. 3, recorded in London by His Master's Voice in June 1932. Prokofiev also recorded some of his solo piano music for HMV in Paris in February 1935; these recordings were issued on CD by Pearl and Naxos. In 1938, he conducted the Moscow Philharmonic Orchestra in a recording of the second suite from his Romeo and Juliet ballet; this performance was also later released on LP and CD. Another reported recording with Prokofiev and the Moscow Philharmonic was of the First Violin Concerto with David Oistrakh as soloist; Everest Records later released this recording on an LP.
Astor Piazzolla

Ástor Pantaleón Piazzolla (March 11, 1921 – July 4, 1992) was an Argentine tango composer and bandoneón player. His oeuvre revolutionized the traditional tango into a new style termed nuevo tango, incorporating elements from jazz and classical music. An excellent bandoneonist, he regularly performed his own compositions with different ensembles.
Piazzolla's nuevo tango was distinct from the traditional tango in its incorporation of elements of jazz, its use of extended harmonies and dissonance, its use of counterpoint, and its ventures into extended compositional forms. As Argentine psychoanalyst Carlos Kuri has pointed out, Piazzolla's fusion of tango with this wide range of other recognizable Western musical elements was so successful that it produced a new individual style transcending these influences. It is precisely this success, and individuality, that makes it hard to pin down where particular influences reside in his compositions, but some aspects are clear. The use of the passacaglia technique of a circulating bass line and harmonic sequence, invented and much used in 17th and 18th century baroque music but also central to the idea of jazz "changes", predominates in most of Piazzolla's mature compositions. Another clear reference to the baroque is the often complex and virtuosic counterpoint that sometimes follows strict fugal behavior but more often simply allows each performer in the group to assert his voice. A further technique that emphasises this sense of democracy and freedom among the musicians is improvisation that is borrowed from jazz in concept, but in practice involves a different vocabulary of scales and rhythms that stay within the parameters of the established tango sound-world. Pablo Ziegler has been particularly responsible for developing this aspect of the style both within Piazzolla's groups and since the composer's death.
Piazzolla's nuevo tango was distinct from the traditional tango in its incorporation of elements of jazz, its use of extended harmonies and dissonance, its use of counterpoint, and its ventures into extended compositional forms. As Argentine psychoanalyst Carlos Kuri has pointed out, Piazzolla's fusion of tango with this wide range of other recognizable Western musical elements was so successful that it produced a new individual style transcending these influences. It is precisely this success, and individuality, that makes it hard to pin down where particular influences reside in his compositions, but some aspects are clear. The use of the passacaglia technique of a circulating bass line and harmonic sequence, invented and much used in 17th and 18th century baroque music but also central to the idea of jazz "changes", predominates in most of Piazzolla's mature compositions. Another clear reference to the baroque is the often complex and virtuosic counterpoint that sometimes follows strict fugal behavior but more often simply allows each performer in the group to assert his voice. A further technique that emphasises this sense of democracy and freedom among the musicians is improvisation that is borrowed from jazz in concept, but in practice involves a different vocabulary of scales and rhythms that stay within the parameters of the established tango sound-world. Pablo Ziegler has been particularly responsible for developing this aspect of the style both within Piazzolla's groups and since the composer's death.
Aladdin

Aladdin is a 1992 animated feature produced by Walt Disney Feature Animation, and released by Walt Disney Pictures on November 25, 1992. The thirty-first animated feature in the Disney animated features canon, the film is based on the Arab folktale of Aladdin and the magic lamp from One Thousand and One Nights. Several characters and plot elements are also based on the 1940 version of The Thief of Bagdad.
The film was directed by John Musker and Ron Clements, both of whom had just finished writing and directing The Little Mermaid (1989). The musical score was written by Alan Menken, with song lyrics written by Howard Ashman and Tim Rice. Aladdin features the voices of Scott Weinger, Jonathan Freeman, Linda Larkin, Frank Welker, Gilbert Gottfried, Douglas Seale, and, as the Genie of the lamp, Robin Williams. Although this was not the first time in which a major actor such as Williams provided voice-over work for an animated film, it was the first major American animated feature film in which particular attention was paid to a celebrity voice cast member, such as a major movie star, in the film as part of its promotion. This has led to a subsequent increased attention to the casts of later productions, as a major element of animated film marketing.
Aladdin was followed by two direct-to-video sequels: The Return of Jafar (1994) and Aladdin and the King of Thieves (1996), and an animated television series, Aladdin, set between the two sequels.
The film was directed by John Musker and Ron Clements, both of whom had just finished writing and directing The Little Mermaid (1989). The musical score was written by Alan Menken, with song lyrics written by Howard Ashman and Tim Rice. Aladdin features the voices of Scott Weinger, Jonathan Freeman, Linda Larkin, Frank Welker, Gilbert Gottfried, Douglas Seale, and, as the Genie of the lamp, Robin Williams. Although this was not the first time in which a major actor such as Williams provided voice-over work for an animated film, it was the first major American animated feature film in which particular attention was paid to a celebrity voice cast member, such as a major movie star, in the film as part of its promotion. This has led to a subsequent increased attention to the casts of later productions, as a major element of animated film marketing.
Aladdin was followed by two direct-to-video sequels: The Return of Jafar (1994) and Aladdin and the King of Thieves (1996), and an animated television series, Aladdin, set between the two sequels.
Bedrich Smetana

Bedřich Smetena. He is considered as the founder of Czech music, pianist, conductor, composer. He was one of the first nationalist composers in the history of music.
James Pierpont

"Jingle Bells", also known as "One Horse Open Sleigh", is one of the best known and commonly sung secular Christmas songs in the world. The song has been translated into many languages. It was written by James Lord Pierpont (1822–1893) and copyrighted under the title 'One Horse Open Sleigh' on September 16, 1857. He was born in Massachusetts, and died in Winter Haven, Florida. He is buried at Laurel Grove Cemetery in Savannah, Georgia. He was inducted into the Songwriters Hall of Fame in 1970.
Final Fantasy

Final Fantasy (ファイナルファンタジー?) is a media franchise created by Hironobu Sakaguchi, and is developed and owned by Square Enix (formerly Squaresoft). The franchise centers on a series of fantasy and science-fantasy console role-playing games (RPGs), but includes motion pictures, anime, printed media, and other merchandise. The series began in 1987 as an eponymous video game developed to save Square from bankruptcy; the game was a success and spawned sequels. The video game series has since branched into other genres such as tactical role-playing, action role-playing, massively multiplayer online role-playing, and racing.
Although most Final Fantasy installments are independent stories with various different settings and main characters, they feature common elements that define the franchise. Such recurring elements include plot themes, character names, and game mechanics. Plots center on a group of heroes battling a great evil while exploring the characters' internal struggles and relationships. Character names are often derived from the history, languages, and mythologies of cultures worldwide.
The series has been commercially and critically successful; it is Square Enix's best selling video game franchise, with more than 85 million units sold, and one of the best-selling video game franchises. It was awarded a star on the Walk of Game in 2006, and holds seven Guinness World Records in the Guinness World Records Gamer's Edition 2008. The series is well known for its innovation, visuals, and music, such as the inclusion of full motion videos, photo-realistic character models, and orchestrated music by Nobuo Uematsu. Final Fantasy has been a driving force in the video game industry. The video game series has affected Square's business practices and its relationships with other video game developers. It has also introduced many features now common in console RPGs and has been credited with helping to popularize RPGs in markets outside Japan.
Although most Final Fantasy installments are independent stories with various different settings and main characters, they feature common elements that define the franchise. Such recurring elements include plot themes, character names, and game mechanics. Plots center on a group of heroes battling a great evil while exploring the characters' internal struggles and relationships. Character names are often derived from the history, languages, and mythologies of cultures worldwide.
The series has been commercially and critically successful; it is Square Enix's best selling video game franchise, with more than 85 million units sold, and one of the best-selling video game franchises. It was awarded a star on the Walk of Game in 2006, and holds seven Guinness World Records in the Guinness World Records Gamer's Edition 2008. The series is well known for its innovation, visuals, and music, such as the inclusion of full motion videos, photo-realistic character models, and orchestrated music by Nobuo Uematsu. Final Fantasy has been a driving force in the video game industry. The video game series has affected Square's business practices and its relationships with other video game developers. It has also introduced many features now common in console RPGs and has been credited with helping to popularize RPGs in markets outside Japan.
Ferdinando Carulli

Ferdinando Maria Meinrado Francesco Pascale Rosario Carulli (February 9, 1770 – February 17, 1841) was one of the most famous composers for classical guitar and the author of the first complete classical guitar method, which continues to be used today. He wrote a variety of works for classical guitar, including concertos and chamber works. He was an extremely prolific writer for guitar, composing over 400 works for the instrument in the space of 12 years.
Carulli was born in Naples, Kingdom of Naples on February 9, 1770. His father, Michele, was a distinguished literator, secretary to the delegate of the Neapolitan Jurisdiction. Like many of his contemporaries, he was taught musical theory by a priest, who was also an amateur musician. Carulli's first instrument was the cello, but when he was twenty he discovered the guitar and devoted his life to the study and advancement of the guitar. As there were no professional guitar teachers in Naples at the time, Carulli developed his own style of playing.
Carulli was a gifted performer. His concerts in Naples were so popular that he soon began touring Europe. Around 1801 Carulli married a French woman, Marie-Josephine Boyer, and had a son with her. A few years later Carulli started to compose in Milan, where he contributed to local publications. After a highly successful Paris tour, Carulli moved there. At the time the city was known as the 'music-capital' of the world, and he stayed there for the rest of his life.
In Paris Carulli became a very successful musician and teacher. He fulfilled his intention of making the guitar popular and fashionable among the upper classes and Paris musicians. It was also in Paris that he published most of his works, eventually becoming a publisher himself and printing the works of other prominent guitarists.
In the 1830s, many European guitarists followed Carulli to Paris, apparently "attracted by his personality". With so many other guitarists in Paris, Carulli worked harder at his teaching, and soon had counted members of the Parisian nobility among his students.
Many of the pieces now regarded as Carulli's greatest were initially turned down by the publishers as being too hard for the average player, and it is likely that many masterpieces were lost this way. Undeterred, Carulli started publishing his pieces himself. However, the great majority of Carulli's surviving works are those that were considered 'safe' enough to be accepted by other publishers, mainly for the teaching of certain techniques or for beginners. Although he had many students and supporters, Carulli began to believe he didn't deserve his impressive reputation because most of the great works he had composed were never published.
Confined to mainly simple pieces, Carulli wrote his world-famous method of classical guitar, "Harmony Applied to the Guitar", a collection of pieces that are still used today in tuition. At the time of publishing, the method was very popular and had many editions published.
Later in life, Carulli began to experiment with changes in guitar construction. With Lacote, a French guitar maker, he made some significant changes for improving the sound of the guitar.
Carulli died in Paris on February 17, 1841, aged 71.
Carulli was born in Naples, Kingdom of Naples on February 9, 1770. His father, Michele, was a distinguished literator, secretary to the delegate of the Neapolitan Jurisdiction. Like many of his contemporaries, he was taught musical theory by a priest, who was also an amateur musician. Carulli's first instrument was the cello, but when he was twenty he discovered the guitar and devoted his life to the study and advancement of the guitar. As there were no professional guitar teachers in Naples at the time, Carulli developed his own style of playing.
Carulli was a gifted performer. His concerts in Naples were so popular that he soon began touring Europe. Around 1801 Carulli married a French woman, Marie-Josephine Boyer, and had a son with her. A few years later Carulli started to compose in Milan, where he contributed to local publications. After a highly successful Paris tour, Carulli moved there. At the time the city was known as the 'music-capital' of the world, and he stayed there for the rest of his life.
In Paris Carulli became a very successful musician and teacher. He fulfilled his intention of making the guitar popular and fashionable among the upper classes and Paris musicians. It was also in Paris that he published most of his works, eventually becoming a publisher himself and printing the works of other prominent guitarists.
In the 1830s, many European guitarists followed Carulli to Paris, apparently "attracted by his personality". With so many other guitarists in Paris, Carulli worked harder at his teaching, and soon had counted members of the Parisian nobility among his students.
Many of the pieces now regarded as Carulli's greatest were initially turned down by the publishers as being too hard for the average player, and it is likely that many masterpieces were lost this way. Undeterred, Carulli started publishing his pieces himself. However, the great majority of Carulli's surviving works are those that were considered 'safe' enough to be accepted by other publishers, mainly for the teaching of certain techniques or for beginners. Although he had many students and supporters, Carulli began to believe he didn't deserve his impressive reputation because most of the great works he had composed were never published.
Confined to mainly simple pieces, Carulli wrote his world-famous method of classical guitar, "Harmony Applied to the Guitar", a collection of pieces that are still used today in tuition. At the time of publishing, the method was very popular and had many editions published.
Later in life, Carulli began to experiment with changes in guitar construction. With Lacote, a French guitar maker, he made some significant changes for improving the sound of the guitar.
Carulli died in Paris on February 17, 1841, aged 71.
Gustav Holst

Gustav Theodore Holst (21 September 1874 – 25 May 1934) was an English composer and was a music teacher for nearly 20 years. He is most famous for his orchestral suite The Planets. Having studied at the Royal College of Music in London, his early work was influenced by Ravel, Grieg, Richard Strauss, and fellow student Ralph Vaughan Williams, but most of his music is highly original, with influences from Hindu spiritualism and English folk tunes. Holst's music is well known for unconventional use of metre and haunting melodies.
Holst wrote almost 200 catalogued compositions, including orchestral suites, operas, ballets, concertos, choral hymns, and songs (see Selected works below).
Holst became music master at St Paul's Girls' School in 1905 and director of music at Morley College in 1907, continuing in both posts until retirement.
He was the brother of Hollywood actor Ernest Cossart and father of the composer and conductor Imogen Holst, who wrote a biography of him in 1938.
Holst wrote almost 200 catalogued compositions, including orchestral suites, operas, ballets, concertos, choral hymns, and songs (see Selected works below).
Holst became music master at St Paul's Girls' School in 1905 and director of music at Morley College in 1907, continuing in both posts until retirement.
He was the brother of Hollywood actor Ernest Cossart and father of the composer and conductor Imogen Holst, who wrote a biography of him in 1938.
Julius Fučík

Julius Ernest Wilhelm Fučík (Czech: ; 18 July 1872 – 25 September 1916) was a Czech composer and conductor of military bands. He became a prolific composer, with over 400 marches, polkas, and waltzes to his name. As most of his work were for military bands, he is sometimes known as the "Bohemian Sousa".Today his marches are still played as patriotic music in the Czech Republic. His worldwide reputation rests primarily on two works: "The Florentiner March", popular throughout much of Europe, and the "Entrance of the Gladiators" (Vjezd gladiátorů), which is widely recognized, often under the title "Thunder and Blazes", as one of the most popular theme tunes for circus clowns.
Gluck

Christoph Willibald Ritter von Gluck (born 2 July 1714 Erasbach, Upper Palatinate; died 15 November 1787 in Vienna) was a composer of the 18th century, most noted for his operatic works. After many years at the Habsburg court at Vienna, Gluck brought about the practical reform of opera's dramaturgical practices that many intellectuals had been campaigning for over the years. With a series of radical new works in the 1760s, among them Orfeo ed Euridice and Alceste, he broke the stranglehold that Metastasian opera seria had enjoyed for much of the century.
The strong influence of French opera in these works encouraged Gluck to move to Paris, which he did in November 1773. Fusing the traditions of Italian opera and the French national genre into a new synthesis, Gluck wrote eight operas for the Parisian stages. One of the last of these, Iphigénie en Tauride, was a great success and is generally acknowledged to be his finest work. Though extremely popular and widely credited with bringing about a revolution in French opera, Gluck's mastery of the Parisian operatic scene was never absolute, and after the poor reception of his Echo et Narcisse, he left Paris in disgust and returned to Vienna to live out the remainder of his life.
The strong influence of French opera in these works encouraged Gluck to move to Paris, which he did in November 1773. Fusing the traditions of Italian opera and the French national genre into a new synthesis, Gluck wrote eight operas for the Parisian stages. One of the last of these, Iphigénie en Tauride, was a great success and is generally acknowledged to be his finest work. Though extremely popular and widely credited with bringing about a revolution in French opera, Gluck's mastery of the Parisian operatic scene was never absolute, and after the poor reception of his Echo et Narcisse, he left Paris in disgust and returned to Vienna to live out the remainder of his life.
Saint Saens
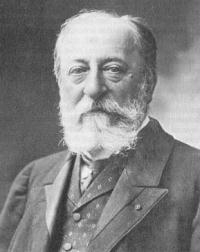
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (9 October 1835 – 16 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor, and pianist, known especially for The Carnival of the Animals, Danse Macabre, Samson and Delilah, Havanaise, Introduction and Rondo capriccioso, and his Symphony No. 3 (Organ Symphony).
Nino Rota

Nino Rota (December 3, 1911, Milan – April 10, 1979, Rome) was a world-renowned Italian composer and academic who is best known for his film scores, notably for the films of Federico Fellini and Luchino Visconti. He also composed the music for two of Franco Zeffirelli's Shakespeare films, and for the first two films of Francis Ford Coppola's Godfather trilogy.
During his long career Rota was an extraordinarily prolific composer, especially of music for the cinema. He wrote more than 150 scores for Italian and international productions from the 1930s until his death in 1979—an average of three scores each year over a 46 year period, and in his most productive period from the late 1940s to the mid-1950s he wrote as many as ten scores every year, and sometimes more, with a remarkable thirteen film scores to his credit in 1954. Alongside this great body film work, he composed ten operas, five ballets and dozens of other orchestral, choral and chamber works, the best known being his string concerto. He also composed the music for many theatre productions by Visconti, Zeffirelli and Eduardo de Filippo as well as maintaining a long teaching career at the Liceo Musicale in Bari, Italy, where he was the director for almost 30 years.
During his long career Rota was an extraordinarily prolific composer, especially of music for the cinema. He wrote more than 150 scores for Italian and international productions from the 1930s until his death in 1979—an average of three scores each year over a 46 year period, and in his most productive period from the late 1940s to the mid-1950s he wrote as many as ten scores every year, and sometimes more, with a remarkable thirteen film scores to his credit in 1954. Alongside this great body film work, he composed ten operas, five ballets and dozens of other orchestral, choral and chamber works, the best known being his string concerto. He also composed the music for many theatre productions by Visconti, Zeffirelli and Eduardo de Filippo as well as maintaining a long teaching career at the Liceo Musicale in Bari, Italy, where he was the director for almost 30 years.
 Sheet Music Drive is a web site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial period.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.
Sheet Music Drive is a web site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial period.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.