Latest Sheet Music
Laurens van rooyen

Laurens van Rooyen (Utrecht, 27 March 1935) is a Dutch pianist and composer. He is known for his cooperation in the theater with Herman van Veen. He composed many pieces for the piano and wrote the score for several Dutch films. He wrote two books on his experiences as a musician.
Lineu Soares

Lineu Soares in Piano from the São Judas Tadeu University (1988) and master in Music from the State University of Campinas (2012). He is currently a University Professor at the Adventist University Center of São Paulo.
Allie Wruble

Elias Paul "Allie" Wrubel was an American composer and songwriter.
Burt Bacharach

Burt Bacharach (born May 12, 1928) is an American pianist and composer. He is best known for his many pop hits from the early 1960s through the 1980s, with lyrics written by Hal David, many of which were produced for and recorded by Dionne Warwick.
As of 2006, Bacharach had written a total of 70 Top 40 hits in the US, and 52 Top 40 hits in the UK. According to britishhitsongwriters.com he is the eighteenth most successful songwriter in U.K. chart history based on weeks that his compositions have spent on the chart.
As of 2006, Bacharach had written a total of 70 Top 40 hits in the US, and 52 Top 40 hits in the UK. According to britishhitsongwriters.com he is the eighteenth most successful songwriter in U.K. chart history based on weeks that his compositions have spent on the chart.
Andrew Lippa

Andrew Lippa (December 22, 1964) is an American composer, lyricist, book writer, performer, and producer. He is a resident artist at the Ars Nova Theater in New York City.
The Corrs

The Corrs are a Celtic folk rock group from Dundalk, County Louth, Ireland. The group consists of the Corr siblings: Andrea (vocals, tin whistle); Sharon (violin, vocals); Caroline (drums, percussion, bodhrán, vocals); and Jim (guitar, keyboards, vocals).
The Corrs came to international prominence with their performance at the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, Georgia. Since then, they have released five studio albums and numerous singles, which have reached platinum in many countries. Talk on Corners, their most successful album to date, reached multi-platinum status in Australia and the UK.
The Corrs have been actively involved in philanthropic activities. They have performed in numerous charity concerts such as the Prince's Trust in 2004 and Live 8 alongside Bono in 2005. The same year, they were awarded honorary MBEs for their contributions to music and charity. The Corrs are on hiatus because Sharon, Jim, and Caroline are raising families, while Andrea is pursuing a solo career.
The Corrs came to international prominence with their performance at the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, Georgia. Since then, they have released five studio albums and numerous singles, which have reached platinum in many countries. Talk on Corners, their most successful album to date, reached multi-platinum status in Australia and the UK.
The Corrs have been actively involved in philanthropic activities. They have performed in numerous charity concerts such as the Prince's Trust in 2004 and Live 8 alongside Bono in 2005. The same year, they were awarded honorary MBEs for their contributions to music and charity. The Corrs are on hiatus because Sharon, Jim, and Caroline are raising families, while Andrea is pursuing a solo career.
Haydn

Franz Joseph Haydn (March 31, 1732 – May 31, 1809) was one of the most prominent composers of the classical period, and is called by some the "Father of the Symphony" and "Father of the String Quartet".
A life-long resident of Austria, Haydn spent most of his career as a court musician for the wealthy Hungarian Esterházy family on their remote estate. Isolated from other composers and trends in music until the later part of his long life, he was, as he put it, "forced to become original".
Although Haydn is still often called "Franz Joseph Haydn", the composer did not use the name "Franz" during his lifetime and this misnomer is avoided by modern scholars and historians. Joseph Haydn was the brother of Michael Haydn, himself a highly regarded composer, and Johann Evangelist Haydn, a tenor.
A central characteristic of Haydn's music is the development of larger structures out of very short, simple musical motifs, often derived from standard accompanying figures. The music is often quite formally concentrated, and the important musical events of a movement can unfold rather quickly.
Haydn's work was central to the development of what came to be called sonata form. His practice, however, differed in some ways from that of Mozart and Beethoven, his younger contemporaries who likewise excelled in this form of composition. Haydn was particularly fond of the so-called "monothematic exposition", in which the music that establishes the dominant key is similar or identical to the opening theme. Haydn also differs from Mozart and Beethoven in his recapitulation sections, where he often rearranges the order of themes compared to the exposition and uses extensive thematic development.
Perhaps more than any other composer's, Haydn's music is known for its humour. The most famous example is the sudden loud chord in the slow movement of his "Surprise" symphony; Haydn's many other musical jokes include numerous false endings (e.g., in the quartets Op. 33 No. 2 and Op. 50 No. 3), and the remarkable rhythmic illusion placed in the trio section of the third movement of Op. 50 No. 1.
A life-long resident of Austria, Haydn spent most of his career as a court musician for the wealthy Hungarian Esterházy family on their remote estate. Isolated from other composers and trends in music until the later part of his long life, he was, as he put it, "forced to become original".
Although Haydn is still often called "Franz Joseph Haydn", the composer did not use the name "Franz" during his lifetime and this misnomer is avoided by modern scholars and historians. Joseph Haydn was the brother of Michael Haydn, himself a highly regarded composer, and Johann Evangelist Haydn, a tenor.
A central characteristic of Haydn's music is the development of larger structures out of very short, simple musical motifs, often derived from standard accompanying figures. The music is often quite formally concentrated, and the important musical events of a movement can unfold rather quickly.
Haydn's work was central to the development of what came to be called sonata form. His practice, however, differed in some ways from that of Mozart and Beethoven, his younger contemporaries who likewise excelled in this form of composition. Haydn was particularly fond of the so-called "monothematic exposition", in which the music that establishes the dominant key is similar or identical to the opening theme. Haydn also differs from Mozart and Beethoven in his recapitulation sections, where he often rearranges the order of themes compared to the exposition and uses extensive thematic development.
Perhaps more than any other composer's, Haydn's music is known for its humour. The most famous example is the sudden loud chord in the slow movement of his "Surprise" symphony; Haydn's many other musical jokes include numerous false endings (e.g., in the quartets Op. 33 No. 2 and Op. 50 No. 3), and the remarkable rhythmic illusion placed in the trio section of the third movement of Op. 50 No. 1.
Katy Perry

Katy Perry (born Katheryn Elizabeth Hudson; October 25, 1984) is an American singer-songwriter. She has risen to prominence with her 2008 single "I Kissed a Girl" which has become a worldwide hit topping the charts in more than 20 countries, including United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, Ireland, and the United States, where it was the 1000th Billboard Hot 100 number 1. Perry has stated in the press that it's thanks to successful British singer-songwriters Amy Winehouse and Lily Allen that more female artists had been appearing on the charts. She went on to say that Winehouse and Allen "have introduced America to great music". She is known for her unconventional style of dress, often humoristic, bright in color and reminiscent of different decades, as well as her frequent use of fruit-shaped accessories, mainly watermelon as part of her outfits. Perry has a contralto vocal range.
Martin Nievera

Martin Ramon Razon Nievera (born February 5, 1962, in Manila, Philippines) is a singer, songwriter, and actor from the Philippines. He is currently working as one of the mainhost of musical variety show ASAP in ABS-CBN
Yoann le Dantec

Yoann Le Dantec, Category: Artist, Albums: Futur antérieur, Imaginary Soundtrack, Vol. 1, Imaginary Soundtrack, Vol. 4, Creative Soundtracks
Herb Alpert & Tijuana Brass
Herb Alpert (born March 31, 1935) is an American jazz musician most associated with the group variously known as Herb Alpert & the Tijuana Brass,
Anna Liani

nna Liani, born in Quebec. During her childhood and adolescence, she has lived in northern Italy, Canada, the Maritimes and Western Canada and Island of ...
Kurt Weill

Kurt Julian Weill was a German Jewish composer, active from the 1920s in his native country, and in his later years in the United States. He was a leading composer for the stage who was best known for his fruitful collaborations with Bertolt Brecht.
Jacques Mazas

Jacques Féréol Mazas was a French composer, conductor, violinist, and pedagogue.
Jules Massenet

Jules (Émile Frédéric) Massenet (May 12, 1842 – August 13, 1912) was a French composer best known for his operas. His compositions were very popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and he ranks as one of the greatest melodists of his era. Soon after his death, Massenet's style went out of fashion, and many of his operas fell into almost total oblivion. Apart from Manon and Werther, his works were rarely performed. However, since the mid-1970s, many operas of his such as Thaïs and Esclarmonde have undergone periodic revivals.
Dr. Lonnie Smith

Lonnie Smith, styled Dr. Lonnie Smith, is an American jazz Hammond B3 organist who was a member of the George Benson quartet in the 1960s. He recorded albums with saxophonist Lou Donaldson for Blue Note before being signed as a solo act. He owns the label Pilgrimage.
Final Fantasy

Final Fantasy (ファイナルファンタジー?) is a media franchise created by Hironobu Sakaguchi, and is developed and owned by Square Enix (formerly Squaresoft). The franchise centers on a series of fantasy and science-fantasy console role-playing games (RPGs), but includes motion pictures, anime, printed media, and other merchandise. The series began in 1987 as an eponymous video game developed to save Square from bankruptcy; the game was a success and spawned sequels. The video game series has since branched into other genres such as tactical role-playing, action role-playing, massively multiplayer online role-playing, and racing.
Although most Final Fantasy installments are independent stories with various different settings and main characters, they feature common elements that define the franchise. Such recurring elements include plot themes, character names, and game mechanics. Plots center on a group of heroes battling a great evil while exploring the characters' internal struggles and relationships. Character names are often derived from the history, languages, and mythologies of cultures worldwide.
The series has been commercially and critically successful; it is Square Enix's best selling video game franchise, with more than 85 million units sold, and one of the best-selling video game franchises. It was awarded a star on the Walk of Game in 2006, and holds seven Guinness World Records in the Guinness World Records Gamer's Edition 2008. The series is well known for its innovation, visuals, and music, such as the inclusion of full motion videos, photo-realistic character models, and orchestrated music by Nobuo Uematsu. Final Fantasy has been a driving force in the video game industry. The video game series has affected Square's business practices and its relationships with other video game developers. It has also introduced many features now common in console RPGs and has been credited with helping to popularize RPGs in markets outside Japan.
Although most Final Fantasy installments are independent stories with various different settings and main characters, they feature common elements that define the franchise. Such recurring elements include plot themes, character names, and game mechanics. Plots center on a group of heroes battling a great evil while exploring the characters' internal struggles and relationships. Character names are often derived from the history, languages, and mythologies of cultures worldwide.
The series has been commercially and critically successful; it is Square Enix's best selling video game franchise, with more than 85 million units sold, and one of the best-selling video game franchises. It was awarded a star on the Walk of Game in 2006, and holds seven Guinness World Records in the Guinness World Records Gamer's Edition 2008. The series is well known for its innovation, visuals, and music, such as the inclusion of full motion videos, photo-realistic character models, and orchestrated music by Nobuo Uematsu. Final Fantasy has been a driving force in the video game industry. The video game series has affected Square's business practices and its relationships with other video game developers. It has also introduced many features now common in console RPGs and has been credited with helping to popularize RPGs in markets outside Japan.
Angelo Badalementi

Angelo Badalamenti, American composer. He composed music for most of the productions directed by David Lynch.
Date of birth: March 22, 1937 (82 years old), Brooklyn, New York, United States Albums: Soundtrack from Twin Peaks, Music of Twin Peaks, Genres: Film score, Jazz, Ambient Music Awards: Grammy Best Pop Instrumental Performance Award, Education: Eastman School of Music, Manhattan School of Music
Date of birth: March 22, 1937 (82 years old), Brooklyn, New York, United States Albums: Soundtrack from Twin Peaks, Music of Twin Peaks, Genres: Film score, Jazz, Ambient Music Awards: Grammy Best Pop Instrumental Performance Award, Education: Eastman School of Music, Manhattan School of Music
Edith Piaf

Édith Piaf (19 December 1915—10 October 1963) was a French singer and cultural icon who "is almost universally regarded as France's greatest popular singer." Her singing reflected her life, with her specialty being the ballads. Among her famous songs are "La vie en rose" (1946), "Hymne à l'amour" (1949), "Milord" (1959), "Non, je ne regrette rien" (1960), and Padam Padam.
Edith Piaf's signature song "La vie en rose" was written in 1945 and was voted a Grammy Hall of Fame Award in 1998.
The legendary Paris Olympia concert hall is where Piaf achieved lasting fame, giving several series of concerts at the hall, the most famous venue in Paris, between January 1955 and October 1962. Excerpts from five of these concerts (1955, 1956, 1958, 1961, 1962) were issued on record and CD and have never been out of print. The 1961 concerts were promised by Piaf in an effort to save the venue from bankruptcy and where she debuted her song "Non, je ne regrette rien". In April 1963, Piaf recorded her last song, "L'homme de Berlin".
Edith Piaf's signature song "La vie en rose" was written in 1945 and was voted a Grammy Hall of Fame Award in 1998.
The legendary Paris Olympia concert hall is where Piaf achieved lasting fame, giving several series of concerts at the hall, the most famous venue in Paris, between January 1955 and October 1962. Excerpts from five of these concerts (1955, 1956, 1958, 1961, 1962) were issued on record and CD and have never been out of print. The 1961 concerts were promised by Piaf in an effort to save the venue from bankruptcy and where she debuted her song "Non, je ne regrette rien". In April 1963, Piaf recorded her last song, "L'homme de Berlin".
Ludwig Van Beethhoven

Ludwig van Beethoven (/ˈlʊdvɪɡ væn ˈbeɪt(h)oʊvən/ (About this soundlisten); German: (About this soundlisten); baptised 17 December 1770 – 26 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. A crucial figure in the transition between the classical and romantic eras in classical music, he remains one of the most recognized and influential musicians of this period, and is considered to be one of the greatest composers of all time.
Beethoven was born in Bonn, the capital of the Electorate of Cologne, and part of the Holy Roman Empire. He displayed his musical talents at an early age and was vigorously taught by his father Johann van Beethoven, and was later taught by composer and conductor Christian Gottlob Neefe. At age 21, he moved to Vienna and studied composition with Joseph Haydn. Beethoven then gained a reputation as a virtuoso pianist, and was soon courted by Prince Lichnowsky for compositions, which resulted in Opus 1 in 1795.
Beethoven was born in Bonn, the capital of the Electorate of Cologne, and part of the Holy Roman Empire. He displayed his musical talents at an early age and was vigorously taught by his father Johann van Beethoven, and was later taught by composer and conductor Christian Gottlob Neefe. At age 21, he moved to Vienna and studied composition with Joseph Haydn. Beethoven then gained a reputation as a virtuoso pianist, and was soon courted by Prince Lichnowsky for compositions, which resulted in Opus 1 in 1795.
Animenz

Animenz Piyanist 17 Mart 1991Anime Piano Works Vol. 1, Anime Piano Works Vol. 2
Laury de Gruyter

Laury de Gruyter nederland composer an Haags Studenten Symfonie Orkest.
George Frideric Handel

George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel (/ˈhændəl/; born Georg Friederich Händel (About this soundlisten); 23 February 1685 (O.S.) – 14 April 1759) was a German, later British, Baroque composer who spent the bulk of his career in London, becoming well known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, and organ concertos. Handel received important training in Halle and worked as a composer in Hamburg and Italy before settling in London in 1712; he became a naturalised British subject in 1727. He was strongly influenced both by the great composers of the Italian Baroque and by the middle-German polyphonic choral tradition.
Edvard Grieg

Edvard Hagerup Grieg (15 June 1843 – 4 September 1907) was a Norwegian composer and pianist who composed in the Romantic period. He is best known for his Piano Concerto in A minor, for his incidental music to Henrik Ibsen's play Peer Gynt (which includes Morning Mood and In the Hall of the Mountain King), and for his collection of piano miniatures Lyric Pieces. "Edvard" is sometimes mispelt as "Edward".
Grieg is renowned as a nationalist composer, drawing inspiration from Norwegian folk music. Early works include a symphony (which he later suppressed) and a piano sonata. He also wrote three sonatas for violin and piano and a cello sonata. His many short pieces for piano — often based on Norwegian folk tunes and dances — led some to call him the "Chopin of the North".
Concerto in A minor: 1. Allegro molto moderato
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 1. Allegro molto moderato
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Concerto in A minor: 2. Adagio
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 2. Adagio
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Concerto in A minor: 3. Allegro moderato molto e marcato
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 3. Allegro moderato molto e marcato
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Notturno, Op. 54, No. 4
Performed live by Mark Gasser
Problems listening to these files? See media help.
The Piano Concerto is his most popular work. Its champions have included the pianist and composer Percy Grainger, a personal friend of Grieg who played the concerto frequently during his long career. An arrangement of part of the work made an iconic television comedy appearance in the 1971 Morecambe and Wise Show, conducted by André Previn.
Some of the Lyric Pieces (for piano) are also well-known, as is the incidental music to Henrik Ibsen's play Peer Gynt, a play that Grieg found to be an arduous work to score properly. In a 1874 letter to his friend Frants Beyer, Grieg expressed his unhappiness with what is now considered one of his most popular compositions from Peer Gynt, In the Hall of the Mountain King: "I have also written something for the scene in the hall of the mountain King - something that I literally can't bear listening to because it absolutely reeks of cow-pies, exaggerated Norwegian nationalism, and trollish self-satisfaction! But I have a hunch that the irony will be discernible."
Grieg is renowned as a nationalist composer, drawing inspiration from Norwegian folk music. Early works include a symphony (which he later suppressed) and a piano sonata. He also wrote three sonatas for violin and piano and a cello sonata. His many short pieces for piano — often based on Norwegian folk tunes and dances — led some to call him the "Chopin of the North".
Concerto in A minor: 1. Allegro molto moderato
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 1. Allegro molto moderato
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Concerto in A minor: 2. Adagio
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 2. Adagio
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Concerto in A minor: 3. Allegro moderato molto e marcato
Performed by the University of Washington Symphony, conducted by Peter Erős (Neal O'Doan, piano)
Concerto in A minor: 3. Allegro moderato molto e marcato
Performed by the Skidmore College Orchestra (courtesy of Musopen)
Notturno, Op. 54, No. 4
Performed live by Mark Gasser
Problems listening to these files? See media help.
The Piano Concerto is his most popular work. Its champions have included the pianist and composer Percy Grainger, a personal friend of Grieg who played the concerto frequently during his long career. An arrangement of part of the work made an iconic television comedy appearance in the 1971 Morecambe and Wise Show, conducted by André Previn.
Some of the Lyric Pieces (for piano) are also well-known, as is the incidental music to Henrik Ibsen's play Peer Gynt, a play that Grieg found to be an arduous work to score properly. In a 1874 letter to his friend Frants Beyer, Grieg expressed his unhappiness with what is now considered one of his most popular compositions from Peer Gynt, In the Hall of the Mountain King: "I have also written something for the scene in the hall of the mountain King - something that I literally can't bear listening to because it absolutely reeks of cow-pies, exaggerated Norwegian nationalism, and trollish self-satisfaction! But I have a hunch that the irony will be discernible."
Pavel Chesnokov

Pavel Grigorievich Chesnokov (Russian: Пáвел Григóрьевич Чеснокóв) (24 October 1877, Voskresensk, Zvenigorod uyezd, Moscow Governorate – 14 March 1944, Moscow), also transliterated Tschesnokoff, Tchesnokov, Tchesnokoff, and Chesnokoff, was an Imperial Russian and Soviet composer, choral conductor and teacher. He composed over five hundred choral works, over four hundred of which are sacred. Today, he is most known for his piece Salvation is Created as well as works such as Do Not Reject Me in Old Age (solo for basso profondo) and movements from various settings of the Divine Liturgy of St John Chrysostom.
Usher

Usher Raymond IV (born October 14, 1978), known simply by his first name Usher, is an American R&B and pop singer-songwriter and actor who rose to fame in the 1990s. To date, he has sold approximately 30 million albums worldwide and has won five Grammy Awards. Usher is a part owner of the Cleveland Cavaliers franchise, and has his own record label, US Records. On September 13, 2008 Usher has been inducted into the All time Hot 100 Artist by the Billboard Hot 100. He is one of the few artists of his generation to be mentioned.
Felix Mendelssohn

Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy, born, and generally known in English-speaking countries, as Felix Mendelssohn (February 3, 1809 – November 4, 1847) was a German composer, pianist, organist and conductor of the early Romantic period.
The grandson of the philosopher Moses Mendelssohn, he was born into a notable Jewish family, although he himself was brought up initially without religion, and later as a Lutheran. He was recognized early as a musical prodigy, but his parents were cautious and did not seek to capitalise on his abilities. Indeed his father was disinclined to allow Felix to follow a musical career until it became clear that he intended to seriously dedicate himself to it.
Early success in Germany was followed by travel throughout Europe; Mendelssohn was particularly well received in England as a composer, conductor and soloist, and his ten visits there, during which many of his major works were premiered, form an important part of his adult career. His essentially conservative musical tastes however set him apart from many of his more adventurous musical contemporaries such as Liszt, Wagner and Berlioz. The Conservatory he founded at Leipzig became a bastion of this anti-radical outlook.
Mendelssohn's work includes symphonies, concerti, oratorios, piano and chamber music. He also had an important role in the revival of interest in the music of Johann Sebastian Bach. After a long period of relative denigration due to changing musical tastes and antisemitism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, his creative originality is now being recognized and re-evaluated. He is now among the most popular composers of the Romantic era.
The grandson of the philosopher Moses Mendelssohn, he was born into a notable Jewish family, although he himself was brought up initially without religion, and later as a Lutheran. He was recognized early as a musical prodigy, but his parents were cautious and did not seek to capitalise on his abilities. Indeed his father was disinclined to allow Felix to follow a musical career until it became clear that he intended to seriously dedicate himself to it.
Early success in Germany was followed by travel throughout Europe; Mendelssohn was particularly well received in England as a composer, conductor and soloist, and his ten visits there, during which many of his major works were premiered, form an important part of his adult career. His essentially conservative musical tastes however set him apart from many of his more adventurous musical contemporaries such as Liszt, Wagner and Berlioz. The Conservatory he founded at Leipzig became a bastion of this anti-radical outlook.
Mendelssohn's work includes symphonies, concerti, oratorios, piano and chamber music. He also had an important role in the revival of interest in the music of Johann Sebastian Bach. After a long period of relative denigration due to changing musical tastes and antisemitism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, his creative originality is now being recognized and re-evaluated. He is now among the most popular composers of the Romantic era.
Bach

Johann Sebastian Bach (31 March 1685 – 28 July 1750) was a German composer and organist whose sacred and secular works for choir, orchestra, and solo instruments drew together the strands of the Baroque period and brought it to its ultimate maturity. Although he introduced no new forms, he enriched the prevailing German style with a robust contrapuntal technique, an unrivalled control of harmonic and motivic organisation in composition for diverse musical forces, and the adaptation of rhythms and textures from abroad, particularly Italy and France.
Revered for their intellectual depth and technical and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg concertos; the Goldberg Variations; the English Suites, French Suites, Partitas, and Well-Tempered Clavier; the Mass in B Minor; the St. Matthew Passion; the St. John Passion; The Musical Offering; The Art of Fugue; the Sonatas and Partitas for violin solo; the Cello Suites; more than 200 surviving cantatas; and a similar number of organ works, including the celebrated Toccata and Fugue in D Minor.
While Bach's fame as an organist was great during his lifetime, he was not particularly well-known as a composer. His adherence to Baroque forms and contrapuntal style was considered "old-fashioned" by his contemporaries, especially late in his career when the musical fashion tended towards Rococo and later Classical styles. A revival of interest and performances of his music began early in the 19th century, and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
Revered for their intellectual depth and technical and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg concertos; the Goldberg Variations; the English Suites, French Suites, Partitas, and Well-Tempered Clavier; the Mass in B Minor; the St. Matthew Passion; the St. John Passion; The Musical Offering; The Art of Fugue; the Sonatas and Partitas for violin solo; the Cello Suites; more than 200 surviving cantatas; and a similar number of organ works, including the celebrated Toccata and Fugue in D Minor.
While Bach's fame as an organist was great during his lifetime, he was not particularly well-known as a composer. His adherence to Baroque forms and contrapuntal style was considered "old-fashioned" by his contemporaries, especially late in his career when the musical fashion tended towards Rococo and later Classical styles. A revival of interest and performances of his music began early in the 19th century, and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
Bryan Adams

Bryan Adams (born Bryan Guy Adams on November 5, 1959) is Grammy Award-winning Canadian singer-songwriter. As of 2008, Adams has released eleven studio albums and 16 albums overall. He has been nominated for 3 Academy Awards and 5 Golden Globes for song writing in motion pictures.
Adams is a Grammy Award-winning Canadian singer-songwriter. Adams' career was launched with his 1980 debut album Bryan Adams, a rock album that garned limited success. His fourth album Reckless was released in 1984 with sales more then five million copies sold in the United States. In 1991, he released Waking Up the Neighbours which debuted at number one on several national music charts. The album reached sales of more than 10 million units worldwide, which 3 million copies was sold in the United States.
Adams is a Grammy Award-winning Canadian singer-songwriter. Adams' career was launched with his 1980 debut album Bryan Adams, a rock album that garned limited success. His fourth album Reckless was released in 1984 with sales more then five million copies sold in the United States. In 1991, he released Waking Up the Neighbours which debuted at number one on several national music charts. The album reached sales of more than 10 million units worldwide, which 3 million copies was sold in the United States.
Ricky Martin

Enrique Martín Morales (born December 24, 1971), better known by his stage name Ricky Martin, is a Grammy Award and Latin Grammy Award-winning Puerto Rican pop singer who rose to fame, first as a member of the Latin boy band Menudo, then as a solo artist since 1991. He has sold more than 55 million albums around the world, charting 21 top-ten hits on the U.S. Latin Charts, eight of which reached number one, and a total of over 30 hit singles.
After several years as a major star in Spanish-speaking countries, Martin prepared his first English album in 1999. The self-titled album contained material by producers such as Desmond Child, Diane Warren, William Orbit and his longtime childhood friend (producer/singer) Robi Draco Rosa. The album also featured special guests Madonna (on the Spanish-English duet "Be Careful (Cuidado con mi Corazón)") and Turkish winner of the 2003 Eurovision Song Contest, Sertab Erener (on the single of his album called "Private Emotion"). The first and most prominent single was "Livin' La Vida Loca," which reached number one in many countries around the world, including the U.S., the U.K., Argentina, Australia, Brazil, France, Turkey, Greece, India, Israel, Italy, Japan, Guatemala, Mexico, Russia, and South Africa. He followed up with the hit "She's All I Ever Had" which impressively peaked at #2 on The Billboard Hot 100. This album became one of the top-selling albums of 1999, and was certified 7 times platinum, selling over 17 million copies worldwide.
On October 11, 2005 Martin released his first English language album since 2000's Sound Loaded and the tenth album of his career. Most of the songs on the album, called Life, were co-written by Martin. He commented on the album: "I was really in touch with my emotions. I think this album is very multi-layered, just like life is. It's about feeling anger. It's about feeling joy. It's about feeling uncertainty. It's about feeling. And all my emotions are part of this production." The album debuted at number six on the Billboard Top 200 Albums chart. The first single from the album was "I Don't Care"/"Qué Más Da", featuring guest appearances by Fat Joe and Amerie.
Martin performed at the 2006 Winter Olympics Closing Ceremony in Turin. A few days later, he announced the second leg of his world tour (which included Europe and Africa) called One Night Only/Una Noche Con Ricky Martin World Tour.
After several years as a major star in Spanish-speaking countries, Martin prepared his first English album in 1999. The self-titled album contained material by producers such as Desmond Child, Diane Warren, William Orbit and his longtime childhood friend (producer/singer) Robi Draco Rosa. The album also featured special guests Madonna (on the Spanish-English duet "Be Careful (Cuidado con mi Corazón)") and Turkish winner of the 2003 Eurovision Song Contest, Sertab Erener (on the single of his album called "Private Emotion"). The first and most prominent single was "Livin' La Vida Loca," which reached number one in many countries around the world, including the U.S., the U.K., Argentina, Australia, Brazil, France, Turkey, Greece, India, Israel, Italy, Japan, Guatemala, Mexico, Russia, and South Africa. He followed up with the hit "She's All I Ever Had" which impressively peaked at #2 on The Billboard Hot 100. This album became one of the top-selling albums of 1999, and was certified 7 times platinum, selling over 17 million copies worldwide.
On October 11, 2005 Martin released his first English language album since 2000's Sound Loaded and the tenth album of his career. Most of the songs on the album, called Life, were co-written by Martin. He commented on the album: "I was really in touch with my emotions. I think this album is very multi-layered, just like life is. It's about feeling anger. It's about feeling joy. It's about feeling uncertainty. It's about feeling. And all my emotions are part of this production." The album debuted at number six on the Billboard Top 200 Albums chart. The first single from the album was "I Don't Care"/"Qué Más Da", featuring guest appearances by Fat Joe and Amerie.
Martin performed at the 2006 Winter Olympics Closing Ceremony in Turin. A few days later, he announced the second leg of his world tour (which included Europe and Africa) called One Night Only/Una Noche Con Ricky Martin World Tour.
Irving Berlin

Irving Berlin (May 11, 1888 – September 22, 1989) was a Russian-born American composer and lyricist, and one of the most prolific American songwriters in history. Berlin was one of the few Tin Pan Alley/Broadway songwriters who wrote both lyrics and music for his songs. Although he never learned to read music beyond a rudimentary level, with the help of various uncredited musical assistants or collaborators, he eventually composed over 3,000 songs, many of which (e.g. "God Bless America", "White Christmas", "Anything You Can Do", "There's No Business Like Show Business") left an indelible mark on music and culture worldwide. He composed seventeen film scores and twenty-one Broadway scores.
Nicollo Paganini

Niccolò (or Nicolò) Paganini (Italian: (About this soundlisten); 27 October 1782 – 27 May 1840) was an Italian violinist, violist, guitarist, and composer. He was the most celebrated violin virtuoso of his time, and left his mark as one of the pillars of modern violin technique. His 24 Caprices for Solo Violin Op. 1 are among the best known of his compositions, and have served as an inspiration for many prominent composers.
Saint Saens
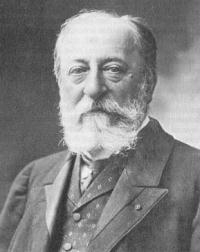
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (9 October 1835 – 16 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor, and pianist, known especially for The Carnival of the Animals, Danse Macabre, Samson and Delilah, Havanaise, Introduction and Rondo capriccioso, and his Symphony No. 3 (Organ Symphony).
Johann Sebastian Bach

Johann Sebastian Bach (31 March 1685 – 28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the Baroque period. He is known for instrumental compositions such as the Art of Fugue, the Brandenburg Concertos, and the Goldberg Variations, and for vocal music such as the St Matthew Passion and the Mass in B minor. Since the 19th-century Bach Revival he has been generally regarded as one of the greatest composers of the Western art musical canon.
Spiral Starecase

The Spiral Starecase was an American pop band, best known for their 1969 single "More Today Than Yesterday". The band, from Sacramento, California, United States, was recognizable for its horns and lead singer/guitarist Pat Upton's voice.
Chopin

Frédéric Chopin (1 March 1810 – 17 October 1849) was a Polish composer and virtuoso pianist of the Romantic period. He is widely regarded as the greatest Polish composer, and ranks as one of music's greatest tone poets.
He was born in the village of Żelazowa Wola, in the Duchy of Warsaw, to a Polish mother and French-expatriate father, and in his early life was regarded as a child-prodigy pianist. In November 1830, at the age of 20, Chopin went abroad; following the suppression of the Polish November Uprising of 1830–31, he became one of many expatriates of the Polish "Great Emigration."
In Paris, he made a comfortable living as a composer and piano teacher, while giving few public performances. A Polish patriot,
Chopin's extant compositions were written primarily for the piano as a solo instrument. Though technically demanding, Chopin's style emphasizes nuance and expressive depth rather than virtuosity. Chopin invented musical forms such as the ballade and was responsible for major innovations in forms such as the piano sonata, waltz, nocturne, étude, impromptu and prelude. His works are mainstays of Romanticism in 19th-century classical music.
He was born in the village of Żelazowa Wola, in the Duchy of Warsaw, to a Polish mother and French-expatriate father, and in his early life was regarded as a child-prodigy pianist. In November 1830, at the age of 20, Chopin went abroad; following the suppression of the Polish November Uprising of 1830–31, he became one of many expatriates of the Polish "Great Emigration."
In Paris, he made a comfortable living as a composer and piano teacher, while giving few public performances. A Polish patriot,
Chopin's extant compositions were written primarily for the piano as a solo instrument. Though technically demanding, Chopin's style emphasizes nuance and expressive depth rather than virtuosity. Chopin invented musical forms such as the ballade and was responsible for major innovations in forms such as the piano sonata, waltz, nocturne, étude, impromptu and prelude. His works are mainstays of Romanticism in 19th-century classical music.
Georges Bizet

Georges Bizet (25 October 1838 – 3 June 1875) was a French composer and pianist of the Romantic era. He is best known for the opera Carmen.
Bizet was born at 26 rue de la Tour d'Auvergne in the 9th arrondissement of Paris in 1838. He was registered with the legal name Alexandre César Léopold Bizet, but he was baptised on 16 March 1840 with the first name Georges, and he was always known thereafter as Georges Bizet. His father Adolphe Armand Bizet (1810-86) was an amateur singer and composer, and his mother, Aimée Léopoldine Joséphine née Delsarte (1814-61), was the sister of the famous singing teacher François Delsarte.
He entered the Paris Conservatory of Music on 9 October 1848, a fortnight before his tenth birthday. His teachers there were Pierre Zimmermann (fugue and counterpoint; often assisted by his son-in-law Charles Gounod), Antoine François Marmontel (piano), François Benoist (organ) and, on Zimmermann's death, Fromental Halévy, whose daughter he himself later married. He won first prizes for organ and fugue in 1855 and completed his earliest compositions.
His first symphony, the Symphony in C, was written in November 1855, when he was seventeen, evidently as a student assignment. It was unknown to the world until 1933, when it was discovered in the archives of the Paris Conservatory library. Upon its first performance in 1935, it was immediately hailed as a junior masterwork and a welcome addition to the early Romantic period repertoire. The symphony bears a stylistic resemblance to the first symphony of Gounod, first played earlier in the same year, and which Bizet had arranged for two pianos although present-day listeners may discern a similarity to music of Franz Schubert, whose work was little known in France at the time the symphony was written.
In 1857, a setting of the one-act operetta Le docteur Miracle won him a share in a prize offered by Jacques Offenbach. He also won the music composition scholarship of the Prix de Rome, the conditions of which required him to study in Rome for three years. There, his talent developed as he wrote such works as the opera buffa Don Procopio (1858-59). There he also composed his only major sacred work, Te Deum (1858), which he submitted to the Prix Rodrigues competition, a contest for Prix de Rome winners only. Bizet failed to win the Prix Rodrigues, and the Te Deum score remained unpublished until 1971. He made two attempts to write another symphony in 1859, but destroyed the manuscripts in December of that year. Apart from this period in Rome, Bizet lived in the Paris area all his life.
Shortly after leaving Rome in July 1860, but while still touring in Italy, he had the idea of writing a symphony in which each of the four movements would be a musical evocation of a different Italian city – Rome, Venice, Florence and Naples. On hearing of his mother's serious illness he cut short his Italian travels and returned to Paris in September 1860; she died a year later. The Scherzo of the symphony was completed by November 1861, but it was not until 1866 that the first version of the whole symphony was written. He subjected it to a number of revisions through to 1871, but died before ever producing what he considered the definitive version. For this reason, the work is sometimes described as "unfinished", but this is an inaccurate description as it was fully scored. It was published in 1880 as the Roma Symphony.
Bizet was born at 26 rue de la Tour d'Auvergne in the 9th arrondissement of Paris in 1838. He was registered with the legal name Alexandre César Léopold Bizet, but he was baptised on 16 March 1840 with the first name Georges, and he was always known thereafter as Georges Bizet. His father Adolphe Armand Bizet (1810-86) was an amateur singer and composer, and his mother, Aimée Léopoldine Joséphine née Delsarte (1814-61), was the sister of the famous singing teacher François Delsarte.
He entered the Paris Conservatory of Music on 9 October 1848, a fortnight before his tenth birthday. His teachers there were Pierre Zimmermann (fugue and counterpoint; often assisted by his son-in-law Charles Gounod), Antoine François Marmontel (piano), François Benoist (organ) and, on Zimmermann's death, Fromental Halévy, whose daughter he himself later married. He won first prizes for organ and fugue in 1855 and completed his earliest compositions.
His first symphony, the Symphony in C, was written in November 1855, when he was seventeen, evidently as a student assignment. It was unknown to the world until 1933, when it was discovered in the archives of the Paris Conservatory library. Upon its first performance in 1935, it was immediately hailed as a junior masterwork and a welcome addition to the early Romantic period repertoire. The symphony bears a stylistic resemblance to the first symphony of Gounod, first played earlier in the same year, and which Bizet had arranged for two pianos although present-day listeners may discern a similarity to music of Franz Schubert, whose work was little known in France at the time the symphony was written.
In 1857, a setting of the one-act operetta Le docteur Miracle won him a share in a prize offered by Jacques Offenbach. He also won the music composition scholarship of the Prix de Rome, the conditions of which required him to study in Rome for three years. There, his talent developed as he wrote such works as the opera buffa Don Procopio (1858-59). There he also composed his only major sacred work, Te Deum (1858), which he submitted to the Prix Rodrigues competition, a contest for Prix de Rome winners only. Bizet failed to win the Prix Rodrigues, and the Te Deum score remained unpublished until 1971. He made two attempts to write another symphony in 1859, but destroyed the manuscripts in December of that year. Apart from this period in Rome, Bizet lived in the Paris area all his life.
Shortly after leaving Rome in July 1860, but while still touring in Italy, he had the idea of writing a symphony in which each of the four movements would be a musical evocation of a different Italian city – Rome, Venice, Florence and Naples. On hearing of his mother's serious illness he cut short his Italian travels and returned to Paris in September 1860; she died a year later. The Scherzo of the symphony was completed by November 1861, but it was not until 1866 that the first version of the whole symphony was written. He subjected it to a number of revisions through to 1871, but died before ever producing what he considered the definitive version. For this reason, the work is sometimes described as "unfinished", but this is an inaccurate description as it was fully scored. It was published in 1880 as the Roma Symphony.
Fernando Lopes Graça

Fernando Lopes-Graça, GOSE, GCIH (17 December 1906 – November 27, 1994) was a Portuguese composer, conductor and musicologist. Lopes-Graça was born in Tomar, and was influenced by Portuguese popular music, which he also studied, continuing the work of the composer and musicologist Francisco de Lacerda. He was a member of the Portuguese Communist Party and strenuously opposed the Estado Novo and its leader António de Oliveira Salazar. He completed the Dicionário de Música (Dictionary of Music), started by his teacher, Tomás Borba, himself a composer. He died in Parede, near Cascais.
Howard Shore

Howard Leslie Shore (born October 18, 1946) is a Canadian composer, notable for his film scores. He has composed the scores for over 40 films, most notably the scores for The Lord of the Rings film trilogy, for which he won three Academy Awards. He is also a consistent collaborator with director David Cronenberg, having scored all but one of his films since 1979. Shore has also worked with Martin Scorsese, Jonathan Demme, David Fincher and many other filmakers.
He has also composed a few concert works including one opera, The Fly, based on the plot (though not his score) of Cronenberg's 1986 film premiered at the Théâtre du Châtelet in Paris on 2 July 2008., a short piece Fanfare for the Wanamaker Organ and the Philadelphia Orchestra, and a short overture for the Swiss 21st Century Symphony Orchestra.
Shore is a three-time winner of the Academy Award, and has also won two Golden Globe Awards and four Grammy Awards. He is the uncle of film composer Ryan Shore.
He has also composed a few concert works including one opera, The Fly, based on the plot (though not his score) of Cronenberg's 1986 film premiered at the Théâtre du Châtelet in Paris on 2 July 2008., a short piece Fanfare for the Wanamaker Organ and the Philadelphia Orchestra, and a short overture for the Swiss 21st Century Symphony Orchestra.
Shore is a three-time winner of the Academy Award, and has also won two Golden Globe Awards and four Grammy Awards. He is the uncle of film composer Ryan Shore.
Théodore-César Salom
Théodore-César Salomé (20 January 1834 – 26 July 1896) was a French organist and composer.Théodore Salomé was born in Paris. He completed all of his musical studies at the Conservatoire de Paris, under the tutelage of François Bazin for harmony and accompaniment, and François Benoist for organ. He won several honorable awards, including: second prize in harmony (1855), second prize in organ and in harmony (1856), second and third prize in harmony and organ (1857), and second prize in harmony (1859). His cantata Atala was awarded the premier Second Grand Prix of the Prix de Rome in 1861. In the same year Théodore Dubois was awarded the first grand prize, and Eugène Anthiome and Titus Constantin won the deuxième Second Grand Prix.
Franz Lehar

Franz Lehár (30 April 1870 – 24 October 1948) was an Austrian composer. He is mainly known for his operettas of which the most successful and best known is The Merry Widow (Die lustige Witwe).
Toto

Toto was a Grammy Award winning American rock band founded in 1977 by some of the most popular and experienced session musicians of the era. The band enjoyed great commercial success in the 1980s, beginning with the band's self-titled debut, released in 1978, which immediately brought the band into the mainstream rock spectrum of the time. Continuing with 1982's critically acclaimed and commercially successful Toto IV, Toto became one of the biggest selling music groups of their era. They also composed the theme music for the film Dune. Although their popularity in the United States diminished in the 1990s and 2000s, they continued to tour to sold out arenas, clubs, and theaters internationally. Toto was known for their technical prowess in the studio, as well as a musical style that combines elements of pop, rock, soul, funk, progressive rock, hard rock, R&B, and jazz, making them appeal to a variety of musicians and non-musician listeners. The band has released 17 albums and has sold over 30 million records to date. Their 18th release Falling In Between Live, was released in August 2007. It had been recorded in March 2007 in Paris. As a result of guitarist Steve Lukather's departure from the band, Toto broke up after the last leg of their 2008 tour.
Tchaikovsky

Pyotr Il'yich Tchaikovsky (May 7 1840 â November 6 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic era. While not part of the nationalistic music group known as "The Five", Tchaikovsky wrote music which, in the opinion of Harold Schonberg, was distinctly Russian: plangent, introspective, with modally-inflected melody and harmony.
Aesthetically, Tchaikovsky remained open to all aspects of Saint Petersburg musical life. He was impressed by Serov and Balakirev as well as the classical values upheld by the conservatory. Both the progressive and conservative camps in Russian music at the time attempted to win him over. Tchaikovsky charted his compositional course between these two factions, retaining his individuality as a composer as well as his Russian identity. In this he was influenced by the ideals of his teacher Nikolai Rubinstein and Nikolai's brother Anton.
Tchaikovsky's musical cosmopolitanism led him to be favored by many Russian music-lovers over the "Russian" harmonies and styles of Mussorgsky, Borodin and Rimsky-Korsakov.
Nonetheless he frequently adapted Russian traditional melodies and dance forms in his music, which enhanced his success in his home country. The success in St. Petersburg at the premiere of his Third Orchestral Suite may have been due in large part to his concluding the work with a polonaise. He also used a polonaise for the final movement of his Third Symphony.
Aesthetically, Tchaikovsky remained open to all aspects of Saint Petersburg musical life. He was impressed by Serov and Balakirev as well as the classical values upheld by the conservatory. Both the progressive and conservative camps in Russian music at the time attempted to win him over. Tchaikovsky charted his compositional course between these two factions, retaining his individuality as a composer as well as his Russian identity. In this he was influenced by the ideals of his teacher Nikolai Rubinstein and Nikolai's brother Anton.
Tchaikovsky's musical cosmopolitanism led him to be favored by many Russian music-lovers over the "Russian" harmonies and styles of Mussorgsky, Borodin and Rimsky-Korsakov.
Nonetheless he frequently adapted Russian traditional melodies and dance forms in his music, which enhanced his success in his home country. The success in St. Petersburg at the premiere of his Third Orchestral Suite may have been due in large part to his concluding the work with a polonaise. He also used a polonaise for the final movement of his Third Symphony.
Whitney Houston

Whitney Elizabeth Houston (born August 9, 1963) is an American singer, actress, and former fashion model. A relative of several prominent soul singers, including her mother Cissy Houston, cousins Dee Dee and Dionne Warwick and godmother Aretha Franklin, Houston began singing at her New Jersey church as a member of a junior gospel choir at age eleven. After she began performing alongside her mother at night clubs in the New York City area, she was discovered by Arista Records label head Clive Davis.
Houston released her debut album Whitney Houston in 1985, which became the best-selling debut album by a female artist at the time of release. Her second studio album Whitney (1987) became the first album by a female artist to debut at number one on the Billboard 200 albums chart. Houston's crossover appeal on the popular music charts as well as her prominence on MTV enabled several African-American women to follow in her success.
Following her marriage to singer Bobby Brown, Houston appeared in her first starring role in the feature film The Bodyguard in 1992. The film's original soundtrack won the 1994 Grammy Award for Album of the Year. Its lead single, Houston's remake of the 1974 Dolly Parton song "I Will Always Love You", became one of the best-selling singles in music history. Houston continued to star in feature films and contributed to soundtracks including Waiting to Exhale (1995) and The Preacher's Wife (1996). After the release of her fourth studio album My Love Is Your Love (1998), she renewed her recording contract with Arista Records in 2001 for a historic $100 million. She subsequently released her fifth studio album, Just Whitney the following year with One Wish: The Holiday Album being released in 2003. Amidst widespread media coverage of personal and professional turmoil, Houston's marriage to Brown ended in 2006.
Houston is one of the world's best-selling music artists, having sold over 190 million albums and singles worldwide. She is ranked as the fourth best-selling female artist in the United States by the Recording Industry Association of America, with 55 million certified albums. She has been listed by Rolling Stone magazine as one of The 100 Greatest Singers of All Time.
Houston released her debut album Whitney Houston in 1985, which became the best-selling debut album by a female artist at the time of release. Her second studio album Whitney (1987) became the first album by a female artist to debut at number one on the Billboard 200 albums chart. Houston's crossover appeal on the popular music charts as well as her prominence on MTV enabled several African-American women to follow in her success.
Following her marriage to singer Bobby Brown, Houston appeared in her first starring role in the feature film The Bodyguard in 1992. The film's original soundtrack won the 1994 Grammy Award for Album of the Year. Its lead single, Houston's remake of the 1974 Dolly Parton song "I Will Always Love You", became one of the best-selling singles in music history. Houston continued to star in feature films and contributed to soundtracks including Waiting to Exhale (1995) and The Preacher's Wife (1996). After the release of her fourth studio album My Love Is Your Love (1998), she renewed her recording contract with Arista Records in 2001 for a historic $100 million. She subsequently released her fifth studio album, Just Whitney the following year with One Wish: The Holiday Album being released in 2003. Amidst widespread media coverage of personal and professional turmoil, Houston's marriage to Brown ended in 2006.
Houston is one of the world's best-selling music artists, having sold over 190 million albums and singles worldwide. She is ranked as the fourth best-selling female artist in the United States by the Recording Industry Association of America, with 55 million certified albums. She has been listed by Rolling Stone magazine as one of The 100 Greatest Singers of All Time.
John Barry

John Barry, OBE (born John Barry Prendergast on 3 November 1933 in York, England) is an English film score composer. He is best known for composing 11 James Bond soundtracks and was hugely influential on the 007 series' distinctive style.
Delta Lea Goodrem

Delta Lea Goodrem (born 9 November 1984) is an Australian singer, songwriter, and actress. Goodrem signed to Sony Music at the age of 15 and released her debut album, Innocent Eyes (2003), which topped the ARIA Albums Chart for 29 consecutive weeks. It was on the List of best-selling albums in Australia, with over four million copies sold.
Goodrem's second album, Mistaken Identity (2004), was created while she was suffering from cancer. It became her second number-one album. In 2007, Goodrem released Delta, her third number-one album, which saw another number-one single, "In This Life". Her fourth studio album, Child of the Universe (2012), produced the single "Sitting on Top of the World". In 2016, her fifth album, Wings of the Wild, became her fourth number-one album on the ARIA Albums Chart, while giving her another number-one single, "Wings".
Goodrem's second album, Mistaken Identity (2004), was created while she was suffering from cancer. It became her second number-one album. In 2007, Goodrem released Delta, her third number-one album, which saw another number-one single, "In This Life". Her fourth studio album, Child of the Universe (2012), produced the single "Sitting on Top of the World". In 2016, her fifth album, Wings of the Wild, became her fourth number-one album on the ARIA Albums Chart, while giving her another number-one single, "Wings".
Amazoness Quartette Theme

The Amazoness Quartet and the Amazon Trio. Her name is derived from the mineral Zirconium dioxide, which is often called Zirconia. Her connection to Nehelenia varies from version to version. In the English-language adaptation, Zirconia's gender was changed from female to male.
Astor Piazzola

Astor Pantaleón Piazzolla (Spanish pronunciation: , Italian pronunciation: ; March 11, 1921 – July 4, 1992) was an Argentine tango composer, bandoneon player, and arranger. His oeuvre revolutionized the traditional tango into a new style termed nuevo tango, incorporating elements from jazz and classical music. A virtuoso bandoneonist, he regularly performed his own compositions with a variety of ensembles.
In 1992, American music critic Stephen Holden described Piazzolla as "the world's foremost composer of tango music"
In 1992, American music critic Stephen Holden described Piazzolla as "the world's foremost composer of tango music"
Balakirev

Mily Alexeyevich Balakirev (Russian: Милий Алексеевич Балакирев, Milij Alekseevič Balakirev, 1910) was a Russian pianist, conductor and composer. He is known today primarily for his work promoting musical nationalism in Russia. Working in conjunction with critic Vladimir Stasov, Balakirev brought together the composers now known as the Five, encouraged their efforts and acted as a musical midwife both for them and for Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky.
Balakirev began his career as a pivotal figure in Russian music by extending and developing the fusion began by Mikhail Glinka of traditional Russian and boldly experimental music. In doing so, he established musical patterns that could express overtly nationalistic feeling. He not only demonstrated in his own works how this could be done, but also by taking amateur musicians of prescribed musical education but enormous potential such as Modest Mussorgsky, Alexander Borodin and Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov, he imparted his own musical beliefs and passed them on to underlie the thinking of his pupils.
Balakirev found himself in an unusual position in his later yers of attending premieres of works he had begun long ago but had only recently completed. For instance, he began writing his First Symphony in 1864 but finished it in 1897. Often, the musical ideas normally associated with Rimsky-Korsakov or Borodin actually originated in Balakirev's compositions. However, his slowness in bringing his works before the public robbed him of credit for his inventiveness. Also, pieces which if completed in the 1860s and 70s would have enjoyed success if they had been performed at that time actually made a much smaller impact when they were introduced toward the end of the composer's life because they had been overtaken by the accomplishments of younger composers. The exception to this is his oriental fantasy Islamey, which is still popular among pianists.
Balakirev began his career as a pivotal figure in Russian music by extending and developing the fusion began by Mikhail Glinka of traditional Russian and boldly experimental music. In doing so, he established musical patterns that could express overtly nationalistic feeling. He not only demonstrated in his own works how this could be done, but also by taking amateur musicians of prescribed musical education but enormous potential such as Modest Mussorgsky, Alexander Borodin and Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov, he imparted his own musical beliefs and passed them on to underlie the thinking of his pupils.
Balakirev found himself in an unusual position in his later yers of attending premieres of works he had begun long ago but had only recently completed. For instance, he began writing his First Symphony in 1864 but finished it in 1897. Often, the musical ideas normally associated with Rimsky-Korsakov or Borodin actually originated in Balakirev's compositions. However, his slowness in bringing his works before the public robbed him of credit for his inventiveness. Also, pieces which if completed in the 1860s and 70s would have enjoyed success if they had been performed at that time actually made a much smaller impact when they were introduced toward the end of the composer's life because they had been overtaken by the accomplishments of younger composers. The exception to this is his oriental fantasy Islamey, which is still popular among pianists.
Guiseppe Cambini

Giuseppe Cambini Giuseppe Maria Gioacchino Cambini was an Italian composer and violinist. Born: February 13, 1746, Livorno, Italy Died: December 29, 1825, Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, France Instruments played: Viola, Violin Record labels: Bongiovanni, Testament, Tudor
Art Tatum

Arthur "Art" Tatum Jr. (October 13, 1909 – November 5, 1956) was an American jazz pianist and virtuoso. He was nearly blind.
Tatum is widely acknowledged as one of the greatest jazz pianists of all time. Critic Scott Yanow wrote, "Tatum's quick reflexes and boundless imagination kept his improvisations filled with fresh (and sometimes futuristic) ideas that put him way ahead of his contemporaries ... Art Tatum's recordings still have the ability to scare modern pianists."
Tatum is widely acknowledged as one of the greatest jazz pianists of all time. Critic Scott Yanow wrote, "Tatum's quick reflexes and boundless imagination kept his improvisations filled with fresh (and sometimes futuristic) ideas that put him way ahead of his contemporaries ... Art Tatum's recordings still have the ability to scare modern pianists."
Mary Poppins

Mary Poppins is an award-winning Disney Theatrical musical based on the similarly-titled series of children's books and the hit Disney 1964 film. The West End production opened in December 2004 and received two Olivier Awards, one for Best Actress in a Musical and the other for Best Theatre Choreography. The musical features the film's music and lyrics by the Academy Award winning Sherman Brothers, along with additional music and lyrics by George Stiles and Anthony Drewe. The book was written by Julian Fellowes. The musical was directed by Richard Eyre and co-directed by Matthew Bourne, who also acted as co-choreographer with Stephen Mear. A Broadway production with a near-identical creative team opened in November 2006, with only minor changes from the West End version.
The stage musical is a fusion of various elements from the film and the books. Some elements from the Mary Poppins series of children's books that had been omitted from the film were restored, such as the walking statue and the ladders rising to the stars. Others were removed, such as the scene in which Uncle Albert gets caught on the ceiling, laughing.
The stage musical is a fusion of various elements from the film and the books. Some elements from the Mary Poppins series of children's books that had been omitted from the film were restored, such as the walking statue and the ladders rising to the stars. Others were removed, such as the scene in which Uncle Albert gets caught on the ceiling, laughing.
 Sheet Music Drive is a web site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial period.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.
Sheet Music Drive is a web site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial period.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.

